Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
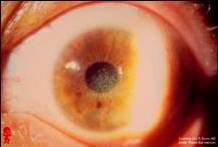 Dominantly inherited, present before age 1. Asymptomatic until later in life; irritation, photophobia, RCEs |
Meesmann's Dystrophy (epithelium)
|
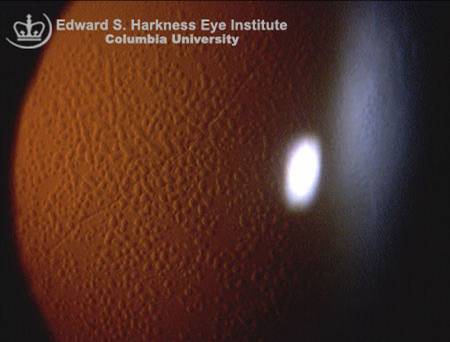 Dominantly inherited, present before age 1. Asymptomatic until later in life; irritation, photophobia, RCEs |
Meesmann's Dystrophy (epithelium)
|
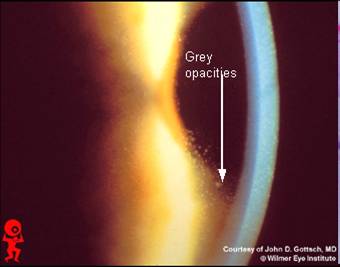 Dominantly inherited, present before age 1. Asymptomatic until later in life; irritation, photophobia, RCEs |
Meesmann's Dystrophy (epithelium)
|
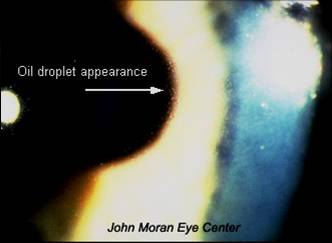 Dominantly inherited, present before age 1. Asymptomatic until later in life; irritation, photophobia, RCEs |
Meesmann's Dystrophy (epithelium)
|
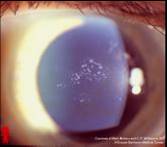 After age 40; bilateral; can be auto-dominant; ghost images, irregular astigmatism, RCEs, visual distortion |
Map-Dot-Fingerprint dystrophy (epithelium)
|
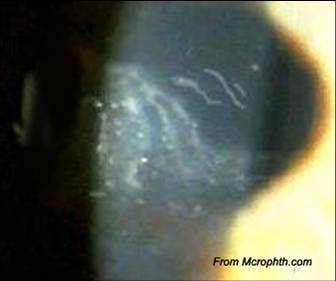 After age 40; bilateral; can be auto-dominant; ghost images, irregular astigmatism, RCEs, visual distortion |
Map-Dot-Fingerprint dystrophy (epithelium)
|
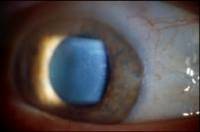 After age 40; bilateral; can be auto-dominant; ghost images, irregular astigmatism, RCEs, visual distortion |
Map-Dot-Fingerprint dystrophy (epithelium)
|
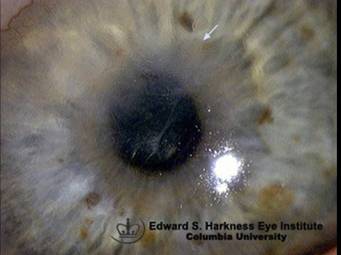 After age 40; bilateral; can be auto-dominant; ghost images, irregular astigmatism, RCEs, visual distortion |
Map-Dot-Fingerprint dystrophy (epithelium)
|
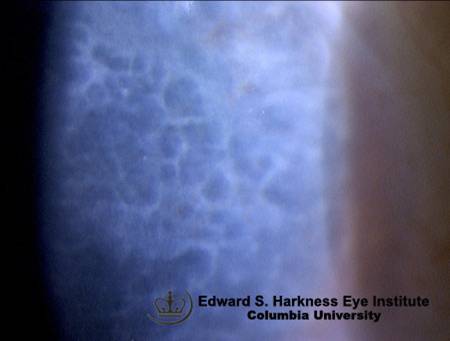 First decade; autosomal dominant; decreased corneal sensitivity, frequent RCEs |
Reis-Buckler Dystrophy or Thiel-Behnke Dystrophy (more honeycombish) - Bowman's layer
|
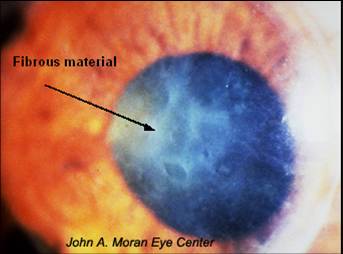 First decade; autosomal dominant; decreased corneal sensitivity, frequent RCEs |
Reis-Buckler Dystrophy or Thiel-Behnke Dystrophy (more honeycombish) - Bowman's layer
|
 First decade; autosomal dominant; decreased corneal sensitivity, frequent RCEs |
Reis-Buckler Dystrophy or Thiel-Behnke Dystrophy (more honeycombish) - Bowman's layer
|
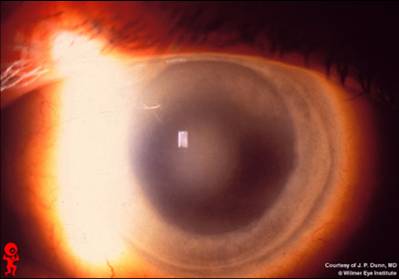 1st-2nd decade; autosomal dominant; starts unilateral becomes bilateral; decreased corneal sensation |
Schnyder's Crystaline dystrophy - Bowman's and stroma affected
|
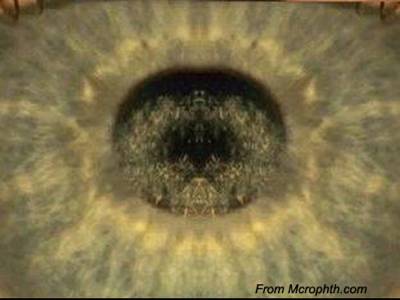 1st-2nd decade; autosomal dominant; starts unilateral becomes bilateral; decreased corneal sensation |
Schnyder's Crystaline dystrophy - Bowman's and stroma affected
|
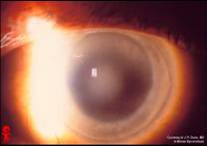 1st-2nd decade; autosomal dominant; starts unilateral becomes bilateral; decreased corneal sensation |
Schnyder's Crystaline dystrophy - Bowman's and stroma affected
|
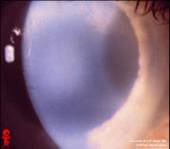 1st-2nd decade; autosomal dominant; starts unilateral becomes bilateral; decreased corneal sensation |
Schnyder's Crystaline dystrophy - Bowman's and stroma affected
|



