Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Anti-Federalists
|
Opposed to the creation of the constitution
|
 Federalists |
Favored the creation of the constitution
|
 US Constitution |
The framework and rules of the current US government
|
 Articles of Confederation |
The United States of America's first government...very weak and ineffective!
|
 Amendments |
changes to the constitution that require both the consent of Congress (national government) and state legislatures
|
 Marbury v. Madison |
Court case that established the principle of Judicial Review
|
 Judicial Review |
Constitutional Principle: judicial branch (courts) decide if govt. acts violate constitution
|
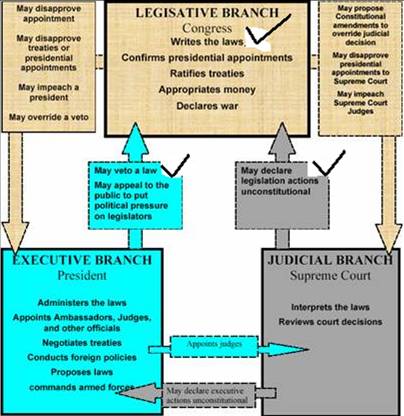 Checks & Balances |
Constitutional Principle: each branch has powers over the other 2 branches--Creates Balanced Branches
|
 Separation of Powers |
Constitutional Principle: govt. power is divided between legislative,executive, & judicial branches
|
 Rule of Law |
Constitutional Principle: laws apply to all people
|
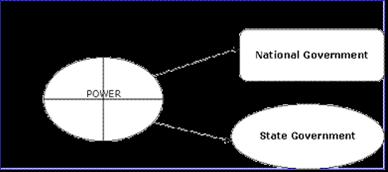 Federalism |
Constitutional Principle: power is divided and shared between national (central), state, local govts.
|
 Popular Sovereignty |
Constitutional Principle: People are the source of government power
|
 Opportunity cost |
- what you could be doing/spending money on, but you chose not to do
- What is the opportunity cost of studying? |
 Mixed-market economy |
-a blend of economies (market & command economies)
-People have economic choices, but the government can regulate these choices! |
 Market economy |
buyers and sellers make economic decisions--NO Government regulation exists!
|



