Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Which annelid group contains broadcast spawners?
|
Polychaetes
|
|
State something about the animal body cavity that is true
|
A larva-may be a herbivore
|
|
Mollusks are highly diverse in?
|
Morphologymodes of nutritionreproductionresponse to environment
|
|
Name some of the characteristics of the phylum mollusca
|
Bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, coelomate protostomes
|
|
What are the major groups of mollusks?
|
-polyplacophora-Gastropoda-Bivalvia-Cephalopoda
|
|
Body Plan of the mollusk
|
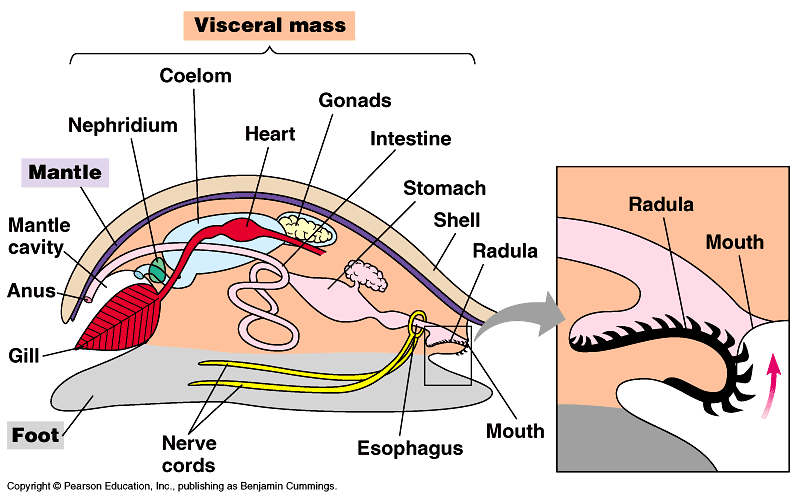 -Visceral mass-mantle-foot |
|
Polyplacophorans
|
-large muscular foot-ability to roll into a ball-gills located in mantle grooves-omnivorious-segmented shellradula scrapes algae and bryozoans
|
|
Bivalvia
|
-mantle cavity modified by siphons-enlargement of gill-relatively sessile-filter feeders-broadcast spawners
|
|
What are siphons?
|
Extension of posterior mantlewater flows in mantle cavity and then across fills that act as filters for food
|
|
What is the foot used in the bivalves for?
|
-anchor and digging
|
|
What are the adductor muscles in scallops used for?
|
Close shell
|
|
What do mantle lined eyes do in scallops?
|
Detect motion and light
|
|
Gastropoda-shelled or shelllish (slugs)
|
Herbivorespredatorsmore complex headinternal and external fertilization -dioecious(gonads separate individuals) or hermaphroditic --can't produce both eggs and sperm at the same time
|
|
What is torsion?
|
-twisting of body(180 degree rotation)mantle cavity anus moved over head
|
|
Coiling of what?
|
Visceral mass
|



