Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Keep
in mind the concepts of osmolarity and tonicity. There will be another
osmolarity problem on the final.
|
Osmolarity
is an easily measurable characteristic, by e.g. freezing point
depression.
In simple terms it is the total concentration of solutes
(including
ions) in a solution, and this does not depend on whether the
solutes
can cross cell membranes or not. Tonicity relates to the osmotic
GRADIENT
due to solutes that affects a semi-permeable membrane ( i.e.
a
membrane that is permeable to water); ONLY solutes that do not cross
the
membrane contribute to this effect.
|
|
Animals
have become pretty good at becoming waterproof but there’s
one
area where water will always be permeable.
What is it
|
The mouth and nose will always be permeable
|
|
Be
able to draw, recognize, and explain a “regulator vs. conformer” graph.
It
may not be for osmoregulation, though
|
Reg. Est. a body
where everything inside is kept at a certain level
Osmoregulator or
conformer keeps blood at certain levelMost marine invertebrates equilibrate their extracellular fluid osmolarity with the ocean water and are therefore called osmoconformers. Other marine animals maintain extracellular fluid osmolarities much lower than seawater and are therefore called osmoregulators
|
|
We
covered three major environmentsA marine, terrestrial, and freshwater. Explain what problems animals face in each,
in terms of ion and
water balance. Which one is the birthplace of animals Which is the
birthplace
of vertebrates
|
|
|
How do fish cope with the problems of freshwater Of saltwater
|
Lose salt through
the gills; pumps send salt outThey drink the water
and they
have salt glands or
pumps which
pump salt out of the creature
and on to the skinMarine mammal -
exceedingly good kidney to get rid of salt or it never drinks;
dietary water; very good at conserving water
Water uptake by osmosis and ion active uptake in gills |
|
Be able to draw and label the parts of a nephron
|
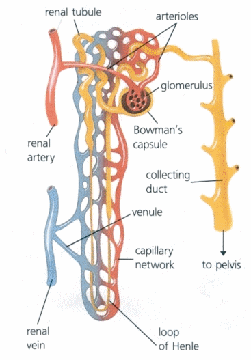 PICTURE |
|
Describe the three functions of a kidney filtration,
resorption, and secretion. What powers filtration What powers resorption
|
|
|
Memorize
how much glucose can there be in a healthy adult human’s urine What is going on when there’s more than that
|
Normal amount of
glucose in a normal adults urine 0
Things in kidneys
resorp glucoseDiabetes mellitus
Sugar in the urine
Caused by excessive
sugar in the blood
|
|
Describe,
briefly, the process of concentration in the loop of Henle, and how this represents
a countercurrent exchanger
|
Loop of henle allows
us to retain water (highly permeable)
Use counter current
exchanger (ensures that water leaves the kidney tubules and come back into the
blood); loop of henle
Fluid that is going
to the collecting duct is more
concentrated
4x as concentrated
|
|
Explain
why nitrogen excretion is a problem, and the three ways animals solve it. Why is nitrogen excretion not a problem for plants
|
If you have an amino
acid you can uses it for energy or other purposes
NH2 is difficult to
let go of because it may produce nh3 in the blood which is toxic
Plants can turn nh3
back into amino acids
To get rid of
ammonia dissolve it in water to get rid of itFish: to get rid of
1 g of ammonia 300 ml of h2o is needed
Mammal: to get rid
of 1 g N 50 ml of h2o is needed (needs ATP)
Uric acid is really
toxic and not soluble in water
To excrete 1g N
takes less than 10 ml water
|



