Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Bias and Variability of Statistics
|
It's unbiased if the mean is equal to the true value of the parameter being estimated.
The variability of a statistic is described by the spread of its sampling distribution, its design and size. |
|
Mean and Standard Deviation of a Sampling Distribution for a Proportion
|
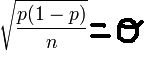 Mean=p |
|
Condition for Using Normal Approximation of a Sampling Distribution for a Proportion
|
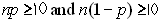 Ensures that normal calculations are accurate enough for most statistical purposes.    |
|
Mean and Standard Deviation of a Sampling Distribution for a Mean
|
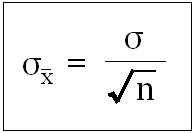 Mean=population mean |
|
Using Normal Approximation of Sampling Distribution for a Mean
|
The sampling distribution is normal if the population is normal and also if it follows the central limit theorem, which is when there are more than 40 observations, the sampling distribution is normal.
|



