Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
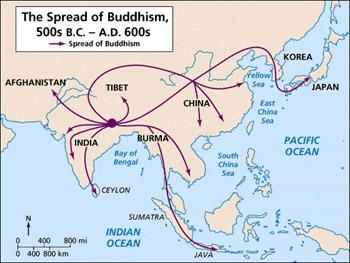 Contagious Diffusion |
1. Definition: Usually associated with the spread of disease, often rapid.
2. Contagious diseases such as influenza have motivated physicians around the world to find a cure for viral infections. Also, people observe items on the internet easily, and can obtain information instantaneously.
3. Example: A Live event on the Internet, where people can directly experience something happening, is a form of contagious diffusion.
|
 Density |
1. Definition: How often an object occurs within a given area or space.
2. Physiological density refers to the total number of people divided by the arable (farmable) land. Arithmetic density calculates the density using all the land in a given area, less accurate than physiological density.
3. Example: Singapore’s population density is far greater than India’s population density, even though India has the larger total population. India has much more land than Singapore, making its density much lower.
|
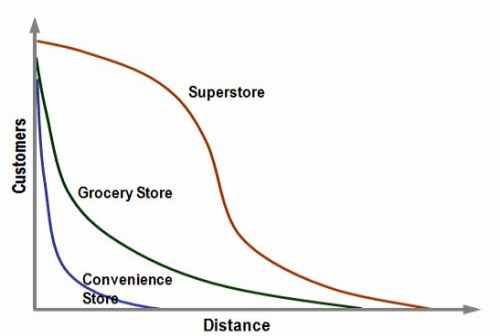 Distance-decay |
1. Definition: A function that represents the way that some influence decays with distance from its geographical location.
2. While people use communication devices such as phones, radio and television broadcasts, and internet, the effects of distance decrease. On the graph, distance-decay is represented by a curving line that swoops concavely downward as distance along the x-axis increases.
3. Example: Once the distance is outside of two people’s activity space, their interactions begin to decrease.
|
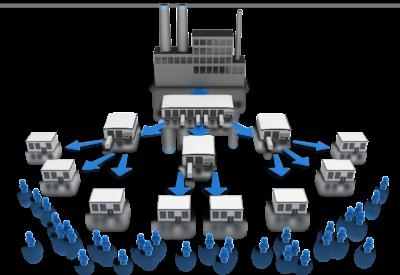 Distribution |
1. Definition: Everything on the Earth’s surface has a physical location and is organized in space in some fashion.
2. Distribution involves anything from buildings, to people, to desks in a classroom. The three aspects of distribution are density, concentration, and pattern.
3. Example: People in a certain region might speak a certain language and they might have a certain pattern.
|
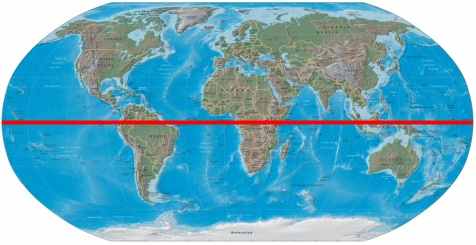 Equator |
|
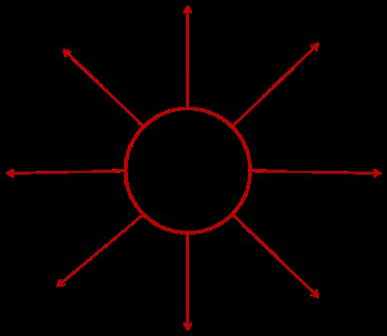 Expansion diffusion |
1. Definition: The spread of characteristics from a central node or a hearth through various means.
2. Expansion diffusion can be separated into three parts of diffusion: hierarchical, contagious, and stimulus diffusion. It is connected to other types of diffusion that were listed above.
3. Example: A contagious diffusion came from expansion diffusion before it was contagious.
|
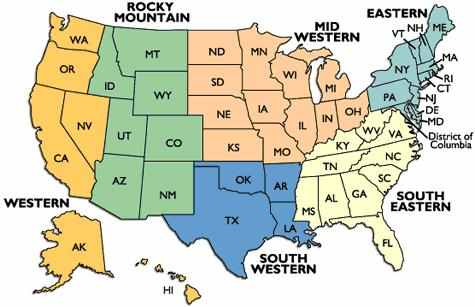 Formal region |
1. Definition: Regions where anything and everything inside has the same characteristic or phenomena.
2. This characteristic may include a language, cultural trait, or religion. People who live in Germany share the characteristic of being subjected to the laws and regulations of Germany.
3. Example: Germany and the Corn Belt are examples of formal regions.
|
 Functional region |
1. Definition: The most intense around the center but lose their characteristics the farther the distance from the vocal point.
2. Functional regions can be defined around a certain point. This region could be described as the area in which one is in range.
3. Example: When you’re driving out of town you listen to the radio, but as you drive further away, you start to lose your connection to the radio station and eventually you do.
|
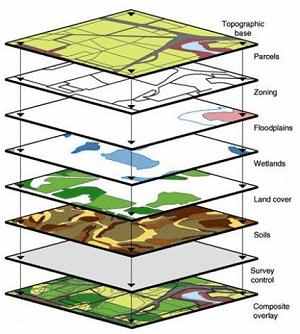 GIS |
1. Definition: (Geographic Information Systems) became practical with the onset of the desktop computer in the 1970s.
2. Data layers are numerical, coded, or textual data that is attributed to specific geographic coordinates/areas. Each data layer can show a different type of geographic features.
3. Example: GIS incorporate one or more data layers in a computer program capable of spatial analysis and mapping.
|
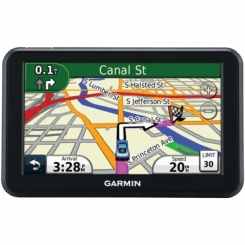 GPS |
1. Definition: (Global Positioning system) that utilizes a worldwide network of satellites, which emit a measurable radio signal.
2. When the signal is available from three or more Navstar satellites, a GPS receiver is able to triangulate a coordination location and display map data for the user. A GPS on an emergency vehicle allows supervisors to see the vehicles location.
3. Example: People use a GPS to find their way to a specific location, or they use it to find a specific vehicle, and or person. It is even used to track certain animals that were tagged.
|
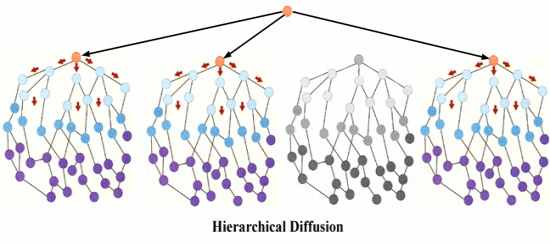 Hierarchical diffusion |
1. Definition: The idea that a phenomenon spreads as a result of a group, usually the social elite, spreading the ideas or patterns in a society.
2. Elite members may be political leaders, entertainment leaders, or sports stars. Elite members of a society often start clothing trends.
3. Example: When a sports star wears a certain outfit or uses a certain gel that becomes a fashion, is hierarchical diffusion.
|
 Hearth |
1. Definition: The place where a certain characteristic began.
2. We often examine how culture, ideas, or technology spread from a point of origin to other parts of the world. It is a point of origin or place of innovation.
3. Example: People born in Britain develop an accent, and when people migrate it spreads across the globe. The spread of Christian belief originated from Jerusalem, and is now practiced worldwide.
|
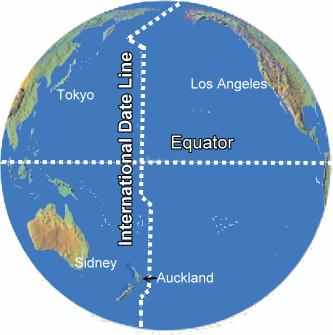 International Date Line |
1. Definition: A line that zigzags its way through the Pacific Ocean owing to the location of countries there.
2. The farthest one can go on the longitude scale is 180 degrees. Longitude roughly represents the International Date Line.
3. Example: The exact location of the line may vary to take into account of other factors, like political boundaries.
|
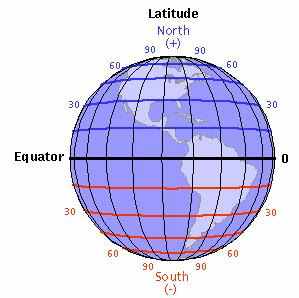 Latitudes |
1. Definition: Parallel lines that run east/west on the surface of the Earth, also known as parallels.
2. The grid system that geographers set up uses latitude and longitude. The Grid system has fictional lines that divide the Earth’s surface to assist people in determining an exact location.
3. Example: 90 degrees north is the North Pole, 90 degrees south is the South Pole.
|
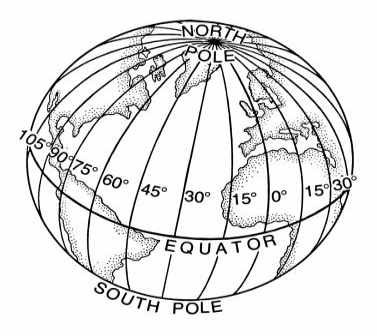 Longitudes |
1. Definition: the lines that run north and south, also known as meridians.
2. The Prime Meridian, zero degrees longitude, runs through Greenwich, in southeast London, England. Greenwich was picked for the Prime Meridian because it was home to observatory that first set up latitude and longitude.
3. Example: For every fifteen degrees longitude traveled east or west, a person will enter a different time zone.
|



