Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Catal huyuk
|
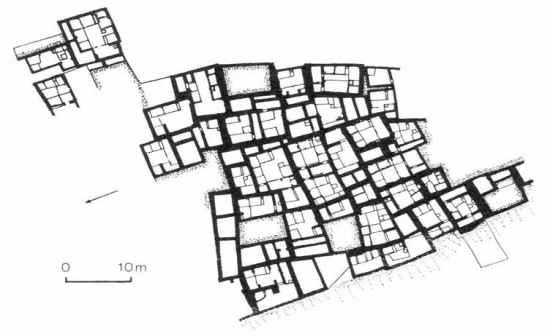 (a)Central room with a hearth (b)Cellular structure (c)Highly organized (d)Enter from top (e)Living space plus storage |
|
Dolmen
|
 (a)Shelter for the dead (b)Entrance, passageway, burial chamber (c)Living need shelter, so too do the dead megalithic tomb: a prehistoric structure thought to have been used as a tomb that consists of a large horizontal slab of stone supported by two or more vertical slab (a)Shelter for the dead (b)Entrance, passageway, burial chamber (c)Living need shelter, so too do the dead such as at Carnac Brittany |
|
Sepulchral
|
Suggesting a tomb or burial
|
|
Nonsepulchral
|
(a)Menhirs – single stones, or ordered in a row
(b)Henge monuments – composed/often circular in plan
|
|
Avebury
|
 (a)Largest constructed structure in Europe prior to industrial revolution (b)420 meters wide (c)11 meter wide ditches (d)Along with Stonehenge and Durrington walls, thought to constitute religious site, dealing with cosmological movement of the sun, moon, as well as the passing of seasons. |
|
stone henge
|
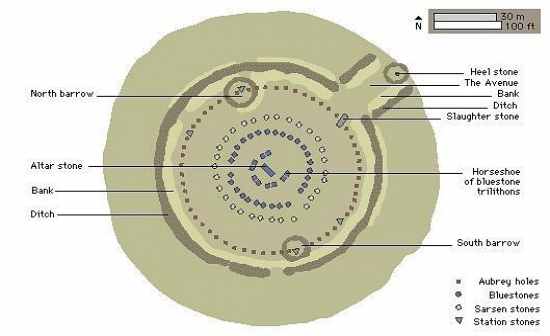 A.Built in 3000B.C. Salisbury Plain, England B.“Blue” Stone transported 140 miles away over water and land from the Prescelly Mountains of South Wales. 1.Altar 2.Horse Shoe Plan, composed of 5 trilithons 3.Beyond trilithons was a circle of smaller uprights made of “blue” stone 4.Outer enclosing circle is the most monumental part of the complex, composed of huge 13 ½ foot tall sandstone 5.The monument was isolated from the surrounding landscape by a trench 6.Heelstone marks cosmic events C.Each lintel was curved to emphasize the curvature of the circle. D.Columns were tapered “entasis” E.Key features 1.Designed for solstice worship 2.Not a burial site 3.Precise construction 4.Demonstrates knowledge of structure F.Space 1.Enclosure but open 2.Centralized yet directional |
|
Mastabas
|
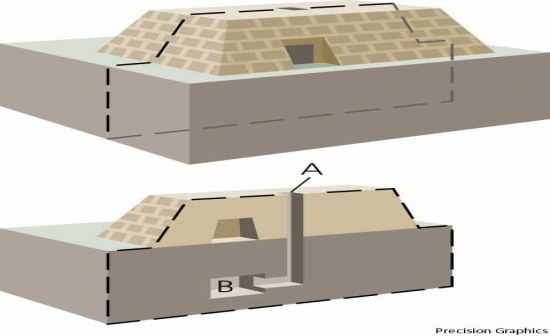 A.Mastabas – earliest above ground structures 1.Mastaba-arabic for “bench” 2.Not less than 30 feet in height 3.Composed of mud brick, with sloped walls 4.Connected to a subterranean burial chamber surrounded by storage rooms |
|
Archaic and Old Kingdom
|
3200-2158 BC
Temples began with mastabas, King Zoser's Step pyramid, and finally mortuary temples such as the Great Pyramid at Giza. |
|
Middle Kingdom
|
2134-1786BC
Tombs returned to earth to avoid grave robbers with the rock-cut tombs. |
|
New Kingdom
|
1570-1085 BC
Sacrificed monumental tombs for shaft tomb in the cliffs of the Valley of the Kings. |
|
Rock-cut tombs
|
 A.Grotto or “Rock-cut” tombs replace exposed tombs that are above ground, because of grave robbers. B.Beni Hasan 2000 B.C. 1.rock-cut tombs are composed of three elements (a)Portico for public worship (b)Chapel in the form of a columnar hall (c)Sepulchral recess |
|
Papyrus column
|
 Have either circular or ribbed shafts, representing single- or multi-stem papyrus plants. The columns may also have either bell shaped capitals (representing the open umbel of the papyrus plant) or closed bud shaped capitals representing the closed papyrus bud. |
|
Lotiform column
|
 columns copy form of lotus plant |
|
Mortuary Temple Plan
|
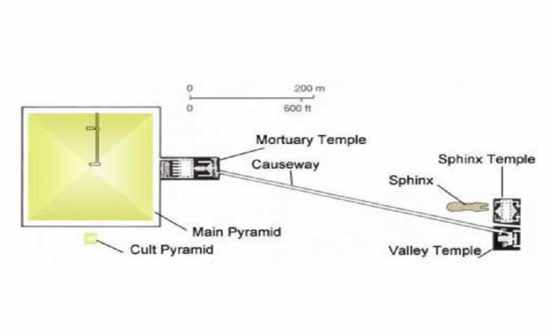 A. develops as Egypt’s most important monument. Designed to commemorate the reign of the pharaoh by whom they were built, as well as for use by the pharaoh’s cult. Built in the vicinity of, royal pyramidal tombs of ancient Egypt. 1.Funerary Temple Complexes (a)Set before the Old Kingdom pyramids (b)Comprised of three interconnected units:
|
|
The Temple of Queen Hatshepsut
|
|



