Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What are viruses? What are they not?
|
Acellular microbes (obligate intracellular parasites)
not cells or organisms
|
|
They can only replicate _____, using ____.
|
Within cells, cell's resources
|
|
How do they metabolize?
|
No metabolism of their own; they "hijack" host cell machinery and cause it to make virus material instead of cell material
|
|
Viruses do not constitute a ______.
They are more diverse than ______, and infect ____.
|
Single taxonomic group
cellular life, every life form
|
|
They are the most ____ biological entities on Earth.
|
Numerous
|
|
We treat viruses not as a _____, but as a special ____ of microbiology.
|
Single group
discipline (virology)
|
|
Viruses are much ____ than bacterial and eukaryotic cells.
|
Smaller
|
|
All viruses have a _____, which is either ___ or ___ and encased in a ______.
|
Genome, DNA or RNA, protein coat (the capsid)
(also single or double stranded)
|
|
Viruses come in a variety of ____.
|
Shapes
|
|
Some viruses
|
West nile, herpes, cowpox, smallpox, ebola, mumps, measles, rabies, papilloma, polio
|
|
What are the 3 basic shapes of viral capsids
|
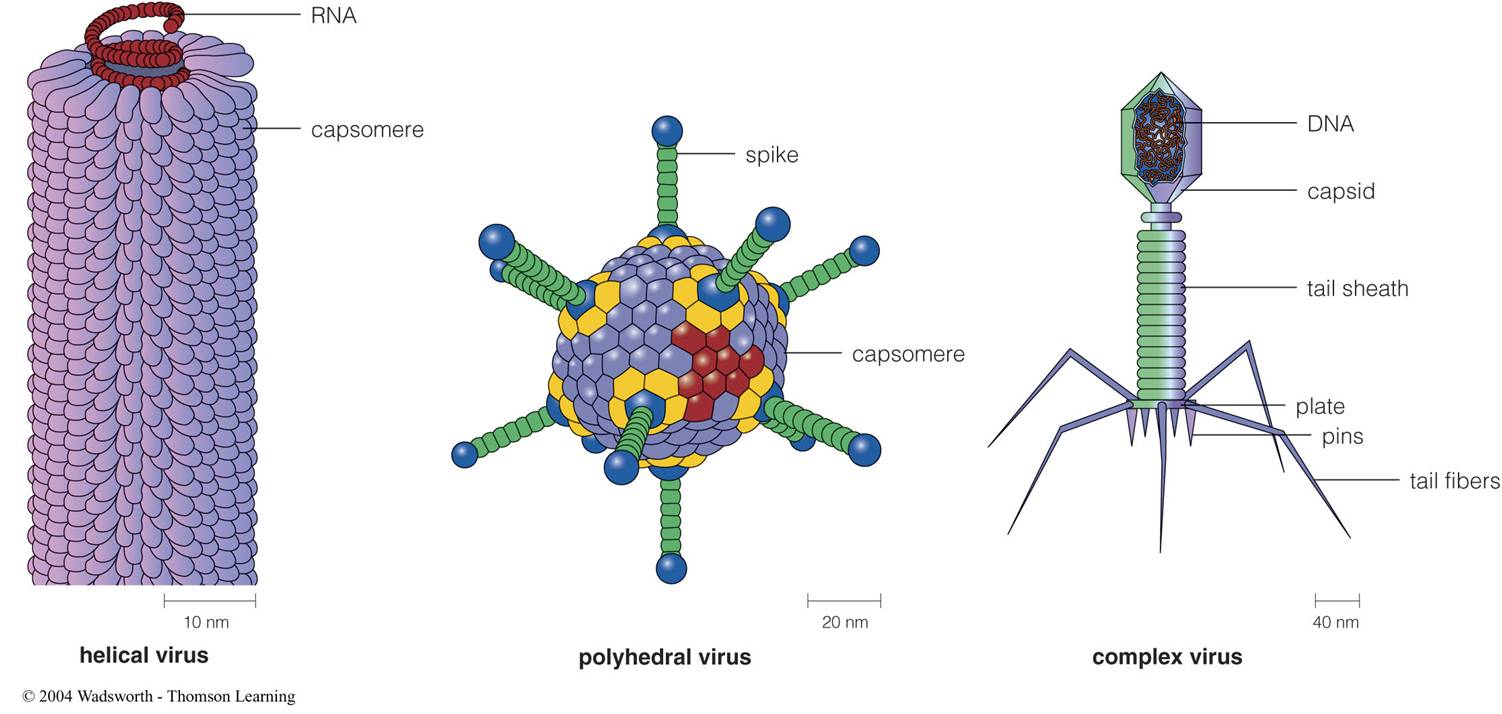 Helical virus polyhedral virus complex virus |
|
Viruses may be ____ or ______ (meaning what?)
|
Envoloped, nonenvoloped
encased in a phospholipid bilayer
|
|
How does lytic replication result in a new generation of virus particles and the death of the host cell?
|
1) viral genome enters host cell
2) viral genome is replicated and transcribed
3) viral mRNAs are translated, and proteins processed
4) particles assemble inside host
5) particles exit to exterior (free particles in tissue or environment)
|
|
What are these steps in more simpler terms?
|
Absorption and entry
biosythesis
assembly
release
|
|
In what ways do viruses emerge from the cell?
|
A) budding of envoloped viruses
b) bursting on non-envoloped viruses
|



