Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What is the chemical definition of “sugar”?
|
A sugar is a polyhydroxyl aldehyde or ketone with 3 or more carbons.
|
|
Glyceraldehyde is the simplest sugar. Draw its chemical structure below.
Another triose happens to be a ketone. What is the structure of this “ketose”? |
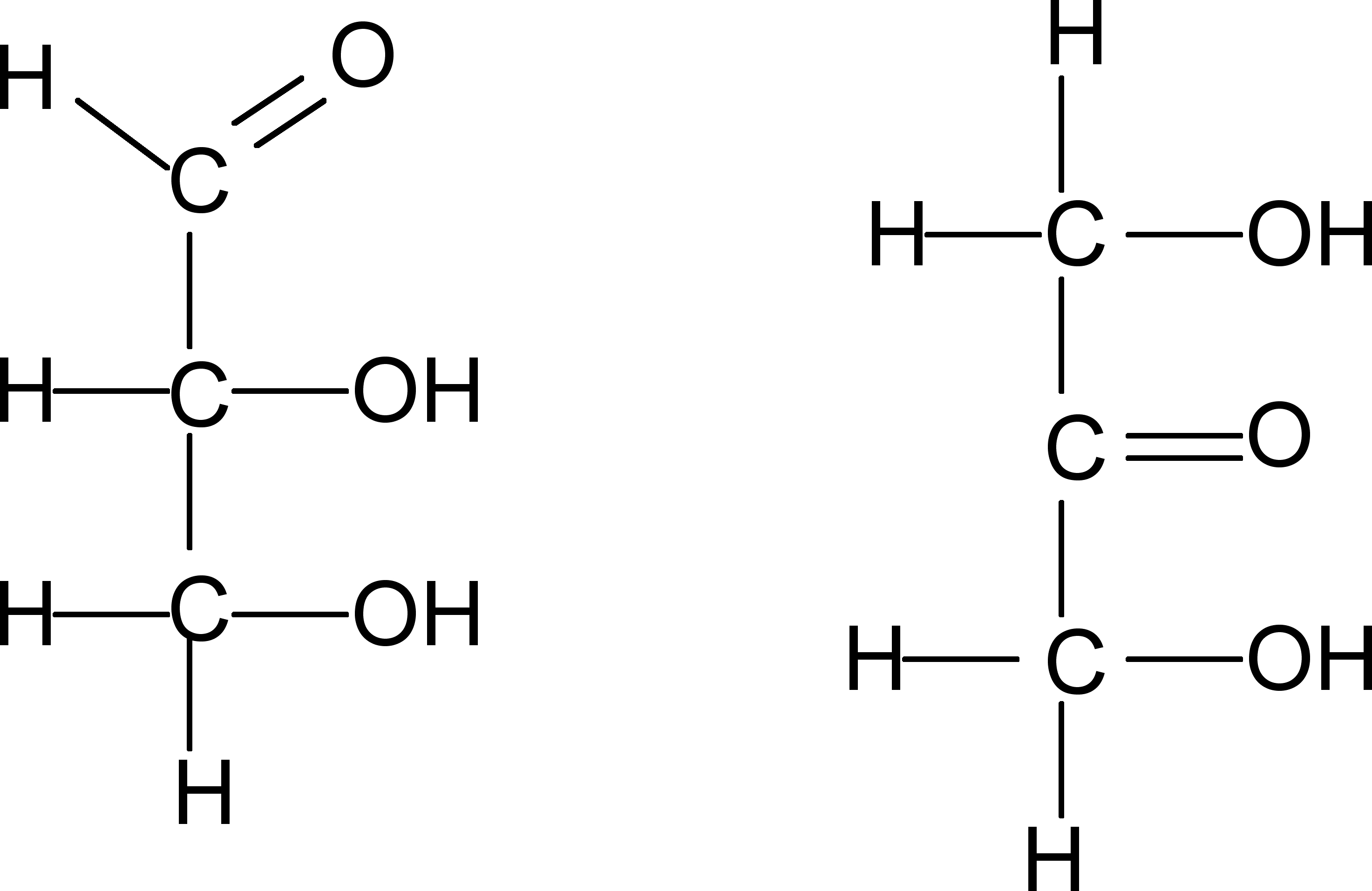 Glyceraldehyde “Ketose” |
|
Glyceraldehyde can easily be converted to an important component of two major classes of lipid. Describe how this happens. Name these two types of lipid and indicate which of these two is the primarily for storage.
|
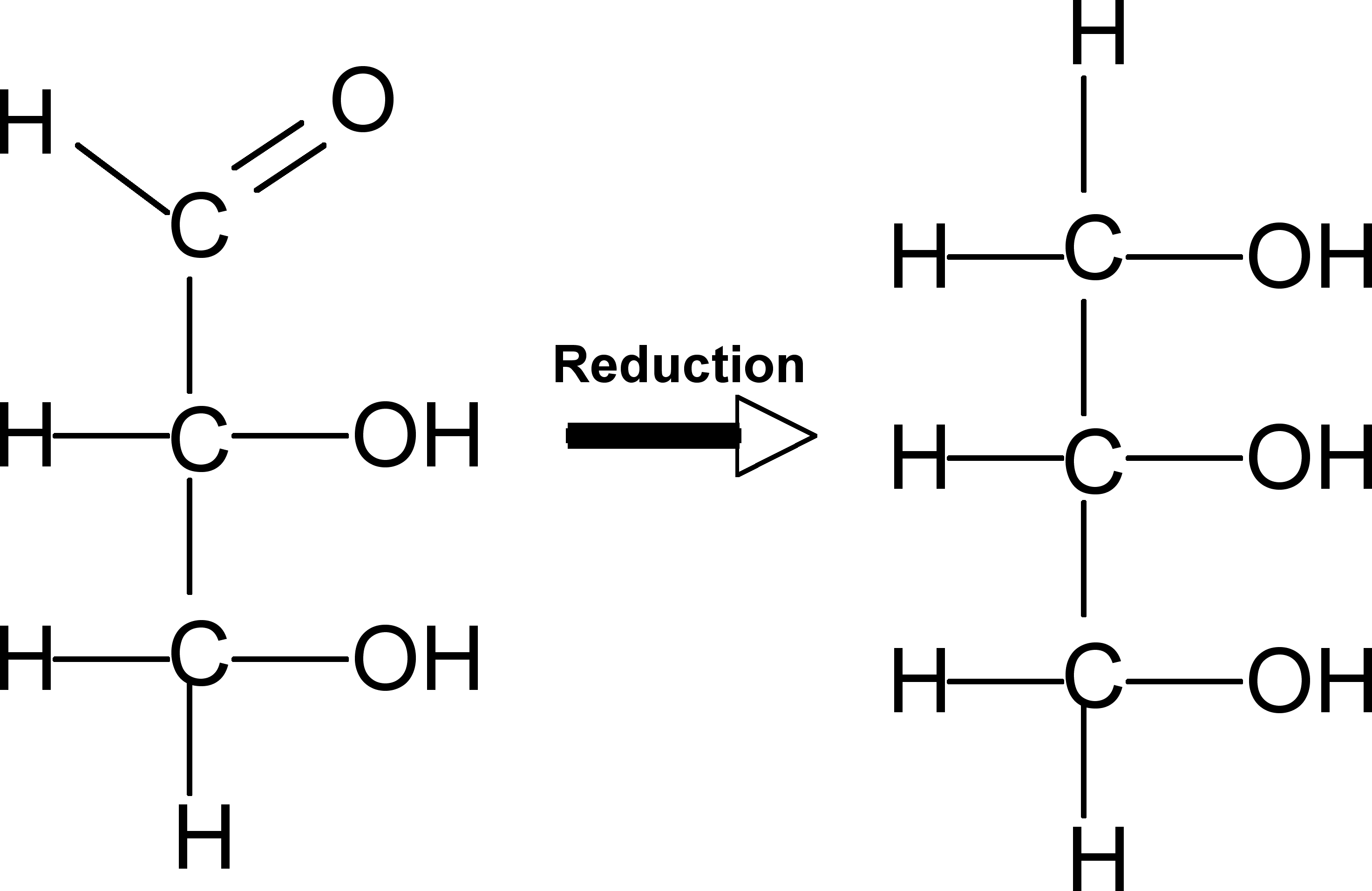 Glyceraldehyde is reduced to glycerol (see below), which is an important part of tri(acyl)glycerides (primarily for storage) and phospholipids. |
|
You probably know that P is present in DNA, RNA and nucleotides. What is the other type major biomolecule that also contains P? Where in this type of macromolecule do you expect to find P?
|
Phosphorus is also present in phospholipids, a subclass of lipids. Phosphorus in the form of phosphate is linked to the third carbon via an ester linkage.
|
|
Mammals lack cellulase, an enzyme that degrades the β-1,4 linkages between glucose molecules in cellulose. However, many mammals (for example, cows and other ruminates) rely on plants materials as foods and derive energy from cellulose. How is this possible?
|
These mammals harbor specific bacteria, which synthesize and secrete cellulases, in their GI tracts. These bacterial enzymes are able to breakdown cellulose, converting it to glucose.
|
|
Plants growing in cold climate tend to produce more unsaturated fatty acids. What is the potential benefit of having unsaturated fatty acids in cold environment? Explain your answer.
|
Unsaturated fatty acids have a “bent” shape due to the presence of double bonds, thus cannot be packed as tightly as saturated fatty acids in the membrane. This increases membrane fluidity to compensate the reduction of fluidity due to cold temperature.
|
|
Oil bodies are major storage organelles for lipids. Oil bodies are surrounded by a unique and exceptional membrane with only one phospholipid layer instead of
the phospholipid bilayer in a typical membrane. Describe how this could happen. |
Oil bodies store tri(acyl)glycerides inside, thus have hydrophobic interior. The membrane covering oil bodies should have a hydrophobic inner surface
in contact with the hydrophobic interior. The hydrophobic tails of a phospholipid monolayer are ideal for interactions with the hydrophobic interior, thus no need to have another phospholipid layer (see diagram below). |
|
The following structure is a glucose. Glucose and another sugar, galactose, differ from each other by having opposite configuration for the hydroxyl group on #4 C. Draw the structure of galactose. The milk sugar, lactose, is a disaccharide made of β-D-galactosyl-(1->4)-α-glucose. Draw the structure of lactose.
|
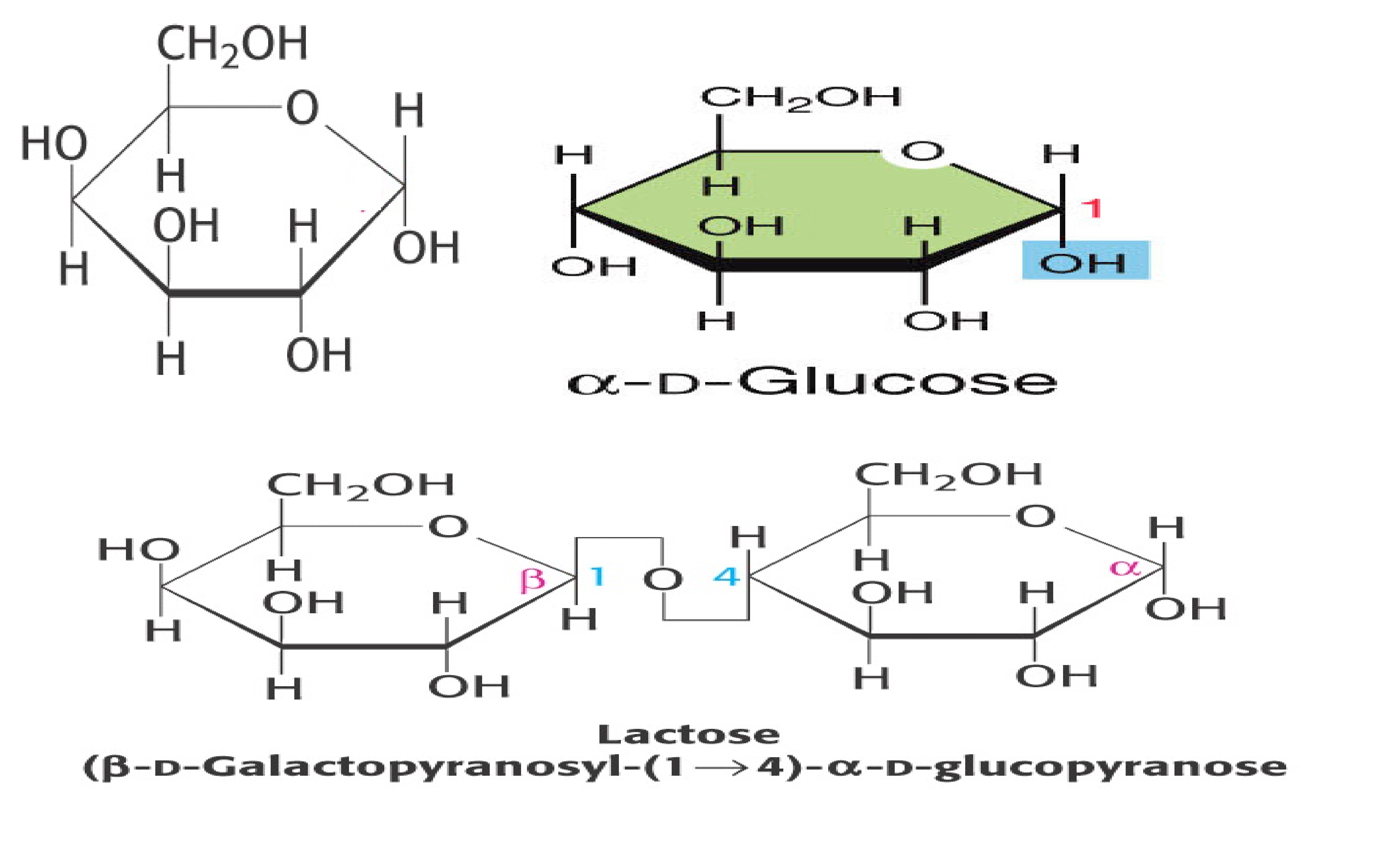 See below |
|
The gelling agent used in jams is called pectin that is a polymer of galacturonic acid (the –OH on #6 carbon of galactose is oxidized to carboxylic acid) linked with each other via α-1.4 linkages. Draw on the structure of galacturonic acid to show 1) the α-hydoxy group involved in polymeration, and 2) the carboxylic group.
|
See key
|
|
Although almost all babies can consume milk, some adults have developed “lactose intolerance”. Describe how this happens.
|
Human babies have lactase enzyme capable of hydrolyzing lactose to galactose and glucose to be further metabolized. However, some adults lose the ability to synthesize this enzyme, thus unable to utilize lactose, which will then be used by bacteria in guts synthesizing another lactose hydrolyzing enzyme, β-galactosidase. Bacteria in guts
using lactose tend to secrete acid and generate gas causing discomfort. |
|
Draw the tripeptide Met-Trp-Leu. Try to draw the backbone without consulting the book before you look up the R group structures on the last page of this problem set. Note that you do not need to memorize R group structures for
the exams – these will be provided. However, you need to know the general structure of amino acids and peptide linkages. |
Look up in the textbook yourself and double check with your classmates
|
|
What is the approximate molecular weight of a protein that contains 550 amino acids? (hint: find info in your textbooks)
|
550 X 110 Dalton (0.11 kD) = 60.5 kD (Although the instructor did not mention this in lectures, this is an important exercise in estimating mol weight of a protein).
|
|
It is relatively easy to make beer (containing at least 5% ethanol) out of corn starch while is kind of hard to produce ethanol out of corn stover (the so called cellulosic ethanol production). What would you do to improve ethanol production from corn stover?
|
The key is in the hydrolysis of polysaccharides (starch and cellulose) to glucose. For starch hydrolysis, it is relatively easy because there are many enzymes capable of doing the job. For cellulose hydrolysis, it is important to
discover cellulose hydrolyzing enzymes in the gut tissue and/or microorganisms living in the guts of wood/grass eating animals, such as termites, cows, and sheep. Once those enzymes are found, mass produce them, and use them to hydrolyze cellulose in corn stover, and use the resulting sugars in the fermentation process for the production of ethanol. |



