Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What are the main parts to the nervous system?
|
Brain and spinal cord - theres senory and motor signals
|
|
Sheep brain- located meninges (sing meninix)
|
- they cover adn protect the brain
- the dura mater - outermost layer, probly removed -arachnoid-middle meninx- thin and delicate bridges the sulci and covers many small blood vessels (not all brains will have this) -pia mater-inner layer-thin vascular membrane applied closely to the brain |
|
Largest portion of the brain ?
raised parts of the brain? deep depression? shallow depressions? |
Cerebrum- surface folded ( two lobes )
outer part- cortex-gray matter raised part- gyri deep- fissures shallow- sulci |
|
Longitudinal fissure
|
Divided the two cerebral hemispheres -> saggital fissure
|
|
Corpus callosum
|
Connects the right and left hemispheres of the brain with nerve fibers
- transverse connections |
|
Secondest largest part of the brain?
|
Cerebellum- more folded than corex ( 1 lobe )
- myelinated nerve fibers leading to the cerebellar cortex can be seen as a white "tree-like" pattern known as arbor vitae. it controls skeletal, muscle contractions required for coordination, posture, balance and fine motor control |
|
Brain stem
|
Connects the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord
|
|
Medulla oblongata
|
Continous with the spinal cord ( most posterior )
|
|
Olfactory bulb
|
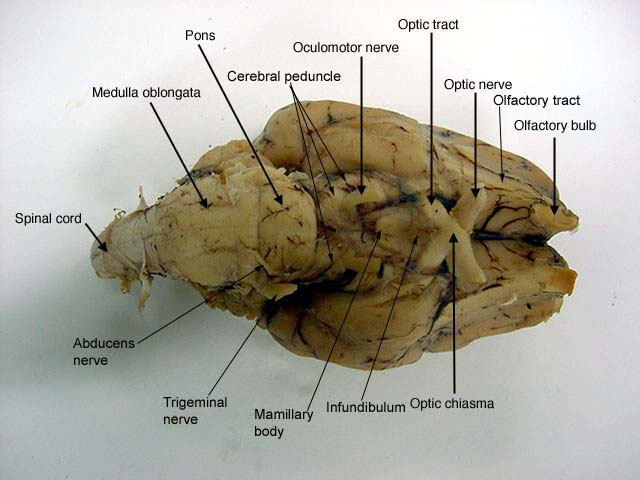 - olfactory bulb and tracts - sense of smell , above the nasal cavity. olfactory nerves extending from the roof of the nasal cavity form synpases with nerons in the olfactory bulb. |
|
Optic chiasma
|
The white cross- posterior to the olfactory tracts. here some of the fobers from each optic nerve cross over to the opposite side of the cerebrum
The optic nerve in here (II)  |
|
Pituitary gland
|
Connected to the main main body of the brain by the pituitary stalk, it lies posterior to the optic chiasma.
|
|
Pons and medulla oblongata
|
Connects parts and is a buldge in the brian, medulla ( posterior to the pons)
pons- relay center for impulses medulla oblongata- involved in the regualtion of heart rate, respiratory rate, and in other basal functions.  |
|
Saggital section: cerebral cortex
|
- sensroy areas which interupt senory impulses, motors areas determine muscular movements, emotional and intellectual thought
 |
|
Thalamus- saggital
|
"central sorting area"- recives senory impulses and relays them to approperiate regions of the brain.
|
|
Pineal gland
|
- small mass of tissue connected to the thalamus - it secretes the hormone melatonin in response too chanign day length.
 |



