Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
A double helix looks like a twisted ladder. Which parts of a twisted ladder are analogous to the hydrogen bonds and the sugar-phosphate backbones of a double helix of DNA?
|
Hydrogen bonds represent the rungs of the ladder. The sugar-phosphate backbone represent the two long sides of the ladder.
|
|
Use Chargaff's rule to determine the approximate percentage of thymine in a DNA molecule, if 28% of the nucleotide in the molecule contain adenine.
|
28%
|
|
( ) concluded that the genetic material of a bacteriophag is DNA.
|
Hershey and Chase
|
|
( ) concluded that DNA was the factor that caused one bacterium to transform into another.
|
Avery
|
|
( ) concluded that bacteria could be transformed from harmless to disease-causing by an unknown factor.
|
Griffith
|
|
The structure of a DNA molecule can be described as a ( )
|
Double helix
|
|
The structure of DNA was discovered by ( ) and ( )
|
James Watson and Francis Crick
|
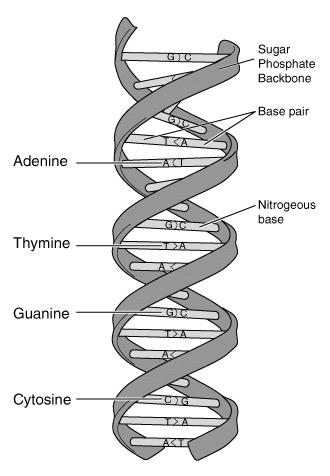 Base pair...Nitrogen base...Sugar-phosphate backbone... |
Hydrogen bondsNucleotideSugar-phosphate backbone.
|
|
Monomer of nuclei acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
|
Nucleotide
|
|
Principle that bonds in DNA can form only between adenine and thymine and between guanine and cytosine.
|
Base Pairing
|
|
Process in which one strain of bacteria is changed by a gene or genes from another strain of bacteria.
|
Transformation
|
|
Virus that infects bacteria.
|
Bacteriophage
|
|
During DNA replication, the DNA molecule ( ) into two strands.
|
Seperates
|
|
At the end of DNA replication, ( ) new stands of DNA have been produced, giving a total of ( ) strands of DNA.
|
Two.four.
|
|
New DNA is replicated in strands complementary to old DNA because production of new DNA follows the rules of ( .)
|
Base-pairing
|



