Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Host A receives a frame and discards it after determining that it is corrupt. At which OSI layer are frames checked for errors?
|
The data-link layer is responsible for checking each frame received for errors. Every Ethernet frame includes the frame check sequence (FCS) or cyclic redundancy check (CRC) value that is calculated by the host which sent the frame.The receiving host generates its own FCS value for every frame received and then compares it with the FCS included in the frame. If the FCS values match, the frame has arrived without any error. If the FCS values do not match, then it is assumed that the frame has an error or is corrupt and, therefore, is discarded.
|
|
Identify which of the services below use both TCP and UDP ports:
|
The domain name service (DNS) protocol is the only protocol of those listed above that uses both the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the User Domain Protocol (UDP). UDP is the preferred transport protocol for DNS services because it's fast. UDP does not require a connection to be established between the hosts before sending any data.If a host fails to receive a response from a DNS server after several requests, it can then switch to TCP. TCP is slower but more reliable, because it requires a three-way handshake to be established between the hosts before any data is sent.
|
|
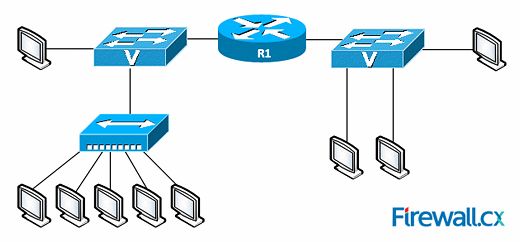
After carefully examining the network diagram above, select the correct statement regarding broadcast and collision domains:
|
There are two broadcast domains and seven collision domains. MORE INFORMATION:Each link to a switch (switch port) is a separate collision domain. In our diagram, we have two switches and a total of seven links. Hubs (located in the lower left corner of the image) do not create separate collision domains per link. That's because traffic entering one port exits all other ports.Routers, on the other hand, create separate broadcast domains as broadcast packets do not propagate across them
|
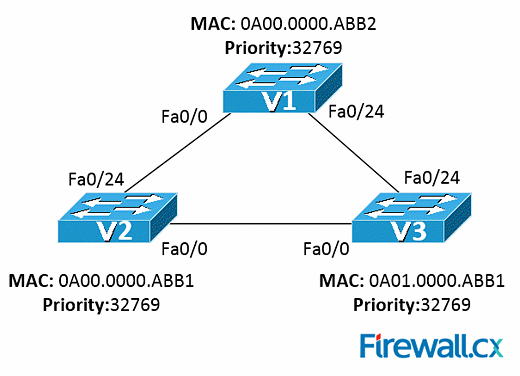 Your manager has requested you indicate which of the above ports will be Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)-designated ports: Your manager has requested you indicate which of the above ports will be Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)-designated ports:
|
Switch V1, Port Fa0/24; Switch V2, Port Fa0/0; Switch V2, Port Fa0/24 MORE INFORMATION:The first step is to understand which switch will become the root switch. This is done via a process called the STP root bridge election process. According to this process, the switch with the lowest bridge ID will be elected as the root switch. In our network diagram, that's SwitchV2.As per STP protocol, SwitchV2 will have all ports set to STP designated. Ports Fa0/0 on SwitchV1 and SwitchV3 are used to reach the root switch and are therefore designated STP root ports.The last set of ports to examine is Fa0/24 on SwitchV1 and SwitchV3. Between these two, one port must be set to blocking mode in order to avoid creating a loop in our network, while the other will be set to forwarding mode. Since SwitchV1 has a lower media access control (MAC) address it wins, so SwitchV1 Fa0/24 is set to forwarding and becomes an STP designated port, while SwitchV3 Fa0/24 turns to a blocking state.
|
|
One of the routers in your company has just received information about network 172.16.10.0/24 from multiple sources. Which of the below will the router consider as the most reliable source for network 172.16.10.0/24?
|
CORRECT ANSWER - A directly connected interface with an IP address of 172.16.10.254/24 MORE INFORMATION:The administrative distance (AD) is used by a router to determine which routing protocol to use if two or more protocols provide routing information for the same destination network. The smaller the administrative distance, the higher the preference.Directly connected interfaces have an AD of 0 and are always preferred. Static routes have an AD of 1, while the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) has an AD of 90 and open shortest path first (OSPF) an AD of 110.
|