Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
NMDA receptor-channels
|
Glutamate receptor and ion channel protein found in nerve cells.
Both ligand-gated and voltage-dependent. Requires co-activation by two ligands: glutamate and either D-serine or glycine. |
|
Mauthner Cell/Neuron
|
A pair of big and easily identifiable neurons in fish and amphibians responsible for their very fast escape reflex. Use chemical and electrical synapses.
|
|
Unilateral neglect
|
Occurs over internal representations of space
|
|
What is optogenetics?
|
A method for turning neurons on or off in transgenic animals (animals with foreign gene inserted into genome) by using light of a specific wavelength.
|
|
Neuron Doctrine
|
Says that neurons are the signaling units of the nervous system.
Says that each neuron is a discrete cell with distinctive processes arising from its cell body. |
|
Emergent Property
|
A property which a collection or complex system has, but which the individual members do not have. aka the whole is greater than the sum of its parts.(second part of the course focuses on these)
|
|
Defining features of hierarchically organized structures:
|
Components are organized.Each part is discrete and precisely positioned with respect to the others.
|
|
Model system for nerve impulses?
|
Squid axon
|
|
Model system for synapses?
|
Frog neuromuscular synapse
|
|
What is Georg von Bekesy known for?
|
He won a Nobel Prize for cochlear transduction, but we focus on his choice to do the blind spot experiment in the dark (revealing that when light is put on the blind spot, a glow emmanates from it)
|
|
Horseshoe Crab details, why we use it.
|
Aka Limulus. More like spider than crab.Hasn't changed much in last 360 million years.4 external eyes - the bundle of all the axons forms the long optic nerve that loops ventrally to the animal's brain. Can study in seawater bath for hours/days.
|
|
Features of limulus eye? How many facets? What are they called?
|
The facets are called ommatidia, and there are 800. Each is about the size of a mechanical pencil tip (0.5mm).
|
|
Ommatidium: structure.
|
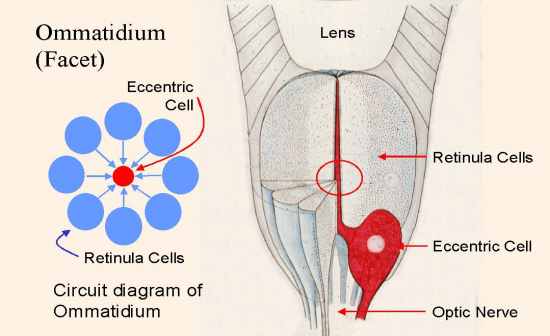 Lens, one dozen retinular cells (like orange segments), single asymmetric "eccentric" cell.Dendrite of the eccentric cell forms the core of the 'tangerine', the axons of the eccentric cells form the optic nerve |
|
What does the ommatidium do?
|
Facet in limulus eye.Retinular cells absorb photons, generate depolarizing potential.Potential flows via gap junctions into eccentric cell. (NOT axons)Summed depolarizations create receptor potential (if large enough, nerve impulse travels to limulus brain) or generator potential (spreads passively until reaches spike initiating zone)
|
|
What happens when light intensity on an ommatidia decreases 10k-fold?
|
Latency (time for it to start firing) increases; frequency reduced but not that much - aka range compression because relationship between intensity and firing is logarithmic.
|



