Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What are Communicable Diseases ?
|
Communicable diseases, also known as infectious diseases or transmissible diseases, are illnesses that result from the infection, presence and growth of pathogenic biologic agents in an individual human or other animal host. Infections may range in severity from asymptomatic to severe and fatal. These diseases can be caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi, etc. Communicable diseases can be transmitted through direct or indirect contact.
|
 Avian Influenza |
Avian influenza , more commonly known as bird flu, is an infectious viral disease of birds, often causing no apparent signs of illness.
TREATMENT :
Evidence suggests that some antiviral drugs, notably oseltamivir, can reduce the duration of viral replication and improve prospects of survival.
In suspected cases, oseltamivir should be prescribed as soon as possible to maximize its therapeutic benefits. However, given the significant mortality currently associated with A(H5N1) and A(H7N9) infection and evidence of prolonged viral replication in this disease, administration of the drug should also be considered in patients presenting later in the course of illness. The use of corticosteroids is not recommended.
|
 Cholera |
Cholera is an acute diarrhoeal infection caused by ingestion of food or water contaminated with the bacterium Vibrio cholerae.
SYMPTOMS : • acute watery diarrhea • severe dehydration TREATMENT : • Prompt administration of oral rehydration salts. • Antibiotics |
 Dengue |
Dengue is a mosquito-borne infection found in tropical and sub-tropical regions around the world.
SYMPTOMS : • high fever • severe headache • joint pains • nausea • rash TREATMENT : No specific treatment for dengue |
 Hepatitis A |
Hepatitis A is a liver disease caused by the hepatitis A virus. The virus is primarily spread when an uninfected (and unvaccinated) person ingests food or water that is contaminated with the faeces of an infected person. The disease is closely associated with a lack of safe water, inadequate sanitation and poor personal hygiene.
SYMPTOMS : • fever • malaise • loss of appetite • nausea • jaundice TREATMENT : • vaccines • improved sanitations |
 Leprosy |
Leprosy is a chronic infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium leprae, an acid-fast, rod-shaped bacillus. The disease mainly affects the skin, the peripheral nerves, mucosa of the upper respiratory tract and also the eyes.
TREATMENT : • Multidrug therapy (MDT) |
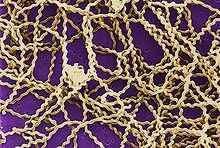 Leptospirosis |
Leptospirosis is an infectious disease caused by bacteria belonging to the genus Leptospira. Leptospirosis occurs worldwide, but is most prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions. Outbreaks can occur following excessive rainfall or flooding.
SYMPTOMS : • The symptoms following infection with leptospira can vary from a mild 'flu'-like illness to a serious and sometimes fatal disease. TREATMENT : • antibiotics |
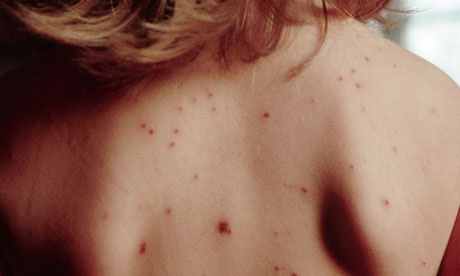 Measles |
Measles is one of the leading causes of death among young children even though a safe and cost-effective vaccine is available.
SYMPTOMS : • fever • runny nose and cough • rash TREATMENT : • vaccine (MMR) |
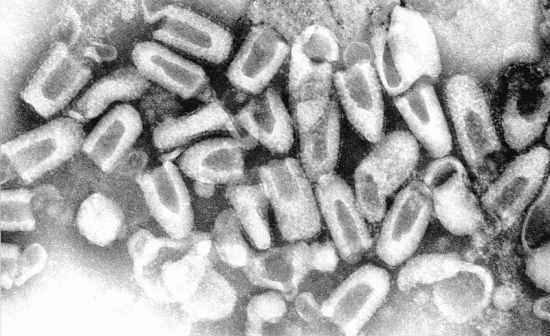 Rabies |
Rabies is a zoonotic disease that is caused by a virus. The disease affects domestic and wild animals, and is spread to people through close contact with infectious material, usually saliva, via bites or scratches.
SYMPTOMS : • fever |
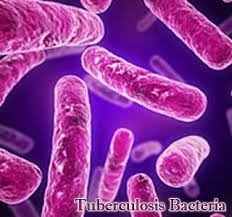 Tuberculosis |
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by bacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) that most often affect the lungs. Tuberculosis is curable and preventable.
SYMPTOMS : • chest pains • weakness • weight loss • fever • nightsweats TREATMENT : • anti microbial drugs |
|
Sources
|
 |



