Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Term:
Reciprocal evolution in interacting species owing to natural selection imposed by each on the other |
Coevolution
|
|
Possible Courses of Coevolution
|
1. Stable Equilibrium
2. Extinction of 1 or both spp 3. Ecological Diversification 4. Red Queen Dynamics |
|
Red Queen Dynamics
|
-->Continuous evolution changes in form of arms race
-->Continuousevolution changes in form of evolutionary cycles |
|
Case: Rough Skinned Newt & Common Garter Snake
|
Ex: Evo arms race
Newt: neurotoxin production Snake: Evolves graduate resistance --> Inc potency of toxin |
|
Evolutionary Cycles (Red Queen Dynamics)
|
Large Predators --> Large prey
Small Pred --> Small Prey Body size of prey/pred cycle theoretical |
|
Case: House Fly & Parasatoid Wasp
|
Ex: test of coevolution (Pred/Prey)
Control: Fly progeny (Host) cannot evolve ---> Cont addition new hosts Exp: Host progeny remain in cage ---> Population responds to parasite (evolution Exp flies can resist wasps better |
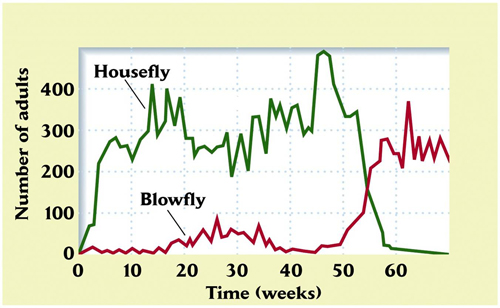 Case: Blowfly & Housefly |
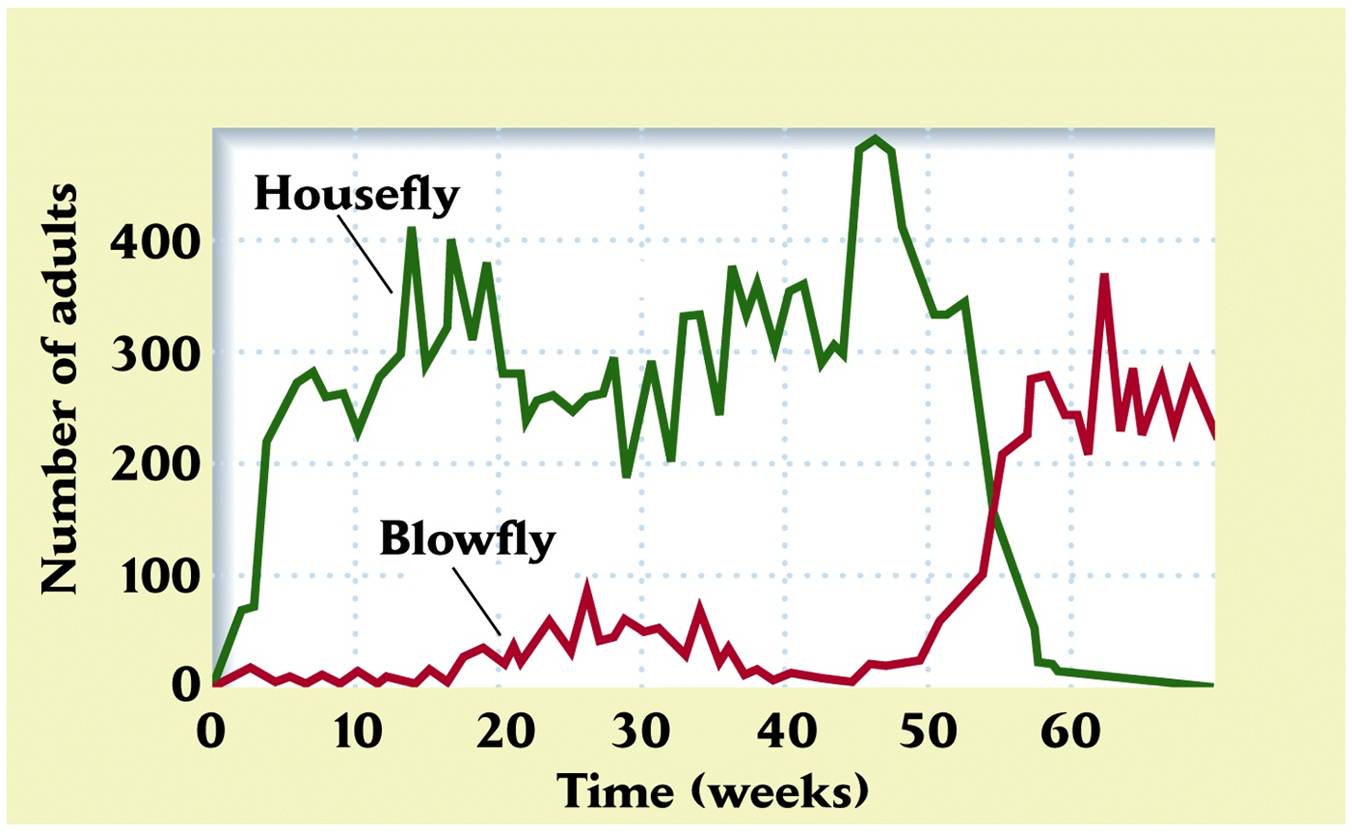 Ex: test of coevolution (Competition) Blowfly = originally worse competitor, but eventually out-competed housefly |
|
Case: Aus Rabit + Myxoma Virus
|
Ex: coevolution in field
1st Myxoma introduction: 99.8% mortality Myxoma: dec lethality --> Chronic infection |
|
Character displacement
|
Consequence of coevolution of competing species
|
|
Parasite
|
Consumes tissue or body fluids of host
|
|
Types of Parasites
|
Pathogens: disease-causing parasites
1. Endoparasites 2. Ectoparasites |
|
Endoparasites
|
Intracellular - in cell
Intercellular - in body cavities tapeworm |
|
Ectoparasites
|
Live outside of Host
e.g. Dodder (plant), Tick |
|
Case: California Estuaries
|
Ex: parasite biomass in ecosystem
% parasite biomass/host: low Biomass density of parasite: comparable to major groups of free-living animals |
|
Ecological Effects of Parasites
|
1. Change Host Behavior
2. Extinction of Host 3. Change Host Population Dynamics 4. Change Outcomes of Competition Interactions 5. Affects Predation 6. Changes Abiotic environment |



