Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
 Michelson, Albert (1852 - 1931) - |
Was an American physicist known for his work on the measurement of the speed of light and especially for the Michelson–Morley experiment. In 1907 he received the Nobel Prize in Physics.
|
|
Michelson's Experiment
|
In any case, the null result of the Michelson–Morley experiment helped the notion of the constancy of the speed of light gain widespread and rapid acceptance.
|
|
Speed of Light (c)
|
299 792 458 m/s or
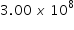 m/s in a vacuum. m/s in a vacuum. |
 Young, Thomas (1773 - 1829) - |
English physician and physicist who established the principle of interference of light and thus resurrected the century-old wave theory of light.
|
|
Photoelectric Effect
|
Is the observation that many metals emit electrons when light shines upon them. Electrons emitted in this manner can be called photoelectrons.
|
|
Einstein, Albert (1879 - 1955) -
|
Proposed that light, and all forms of electromagnetic radiation consists of packets of energy (photons).
|
 Photons |
A particle representing a quantum of light or other electromagnetic radiation. A photon carries energy proportional to the radiation frequency but has zero rest mass.
|
 Intensity |
Is the rate at which a wave's energy flows through given unit of AREA. Intensity is the measurable amount of a property, such as force, brightness, or a magnetic field.
|
 Herschel, Fredick William (1738 - 1822) - |
Pioneered the use of astronomical spectrophotometry as a diagnostic tool, using prisms and temperature measuring equipment to measure the wavelength distribution of stellar spectra. In addition, Herschel discovered infrared radiation.
|
 Electromagnetic (EM) Spectrum - |
Is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation, which subsumes visible light, as well as invisible radiations such as radio waves, infrared light and X rays.
|
|
Radio Waves
|
An electromagnetic wave of a frequency between about 104 and 1011 or 1012 Hz, as used for long-distance communication.
|
|
Amplitude Modulation (AM) -
|
The modulation of a wave by varying its amplitude, used chiefly as a means of radio broadcasting, in which an audio signal is combined with a carrier wave. (530 kHz to 1605 kHz)
|
|
Frequency Modulation (FM) -
|
The modulation of a radio or other wave by variation of its frequency, especially to carry an audio signal. FM stations use frequencies between 88 MHz to 108 MHz.
|
|
Television broadcast
|
An electronic system of transmitting transient images of fixed or moving objects together with sound over a wire or through space by apparatus that converts light and sound into electrical waves and reconverts them into visible light rays and audible sound.
|
 Microwaves |
An electromagnetic wave with a wavelength in the range 0.001–0.3 m, shorter than that of a normal radio wave but longer than those of infrared radiation. Microwaves are used in radar, in communications, and for heating in microwave ovens.
|



