Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Etiology of this is EMBRYOGENIC.
|
Craniopharyngioma
|
|
Etiology of this is cystic or solid tissue, could be intrasellar or suprasellar. (tumor)
|
Craniopharyngioma
|
|
Clinical features: GH & Gonadotropin def., Diabetes insipidus, inc. cranial presure, dec. visual acuity, + more in relation to homeostasis
|
Craniopharyngioma
|
|
Treatment for craniopharyngioma is.....
|
Removing of the tumor (resection os not feasible)
|
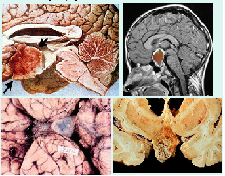 What is this of? |
Craniopharyngioma
|
 What is this of? |
Craniopharyngioma
|
|
Tumors of the pituitary gland that constitute about 5-10% of intracranial tumors
|
Sellar/Suprasellar tumors- Pituitary adenoma
|
|
Eosinophilic cells (tumors) produce excess amounts of.....
|
PRL --> amenorrhoes, galactorrhoea, impotence, infertility and produces: GH --> acromegaly (remember by E.P.G.- Eileen watches PG movies)
|
|
Basophilic cells (tumors) produce excess amounts of....
|
TSH, Gonadotrophins, and ACTH--> cushing's disease
|
|
Chromophobe cells (tumors) produce excess amounts of....
|
Nothing, they are non functioning
|
|
Sellar/suprasellar tumors- pituitary adenoma, HYPOSECRETION is also called:
|
Panhypopituitarism
|
|
______ occurs when more thatn 80% of the pituitary is destroyed.
|
Panhypopituitarism
|
|
Pituitary apoplexy is caused by ______, leading to severe headache, visual failure, altered consciousness, death
|
Hemorrhage into the tumor
|
|
Treatment for PITUITARY APOPLEXY
|
Glucocorticoid treatment: hydrocortisone (anti-inflammatory)
then surgery
|
|
To operative approaches to reach the pituitary gland
|
Trans- sphenoidal and trans- frontal
|



