Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What is a cell?
|
The building blocks of animals and plants
The smallest unit that performs all physiological functions (MRSGREN) Each cell maintains its own and the bodys homeostasis |
|
Draw and label a diagram of the structures of a generalised cell.
|
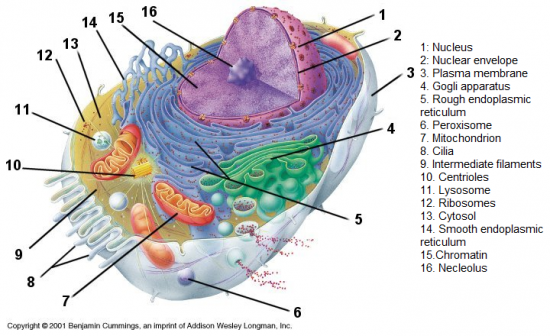 |
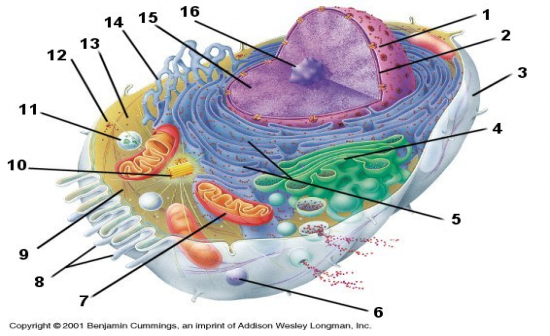 Lable this diagram |
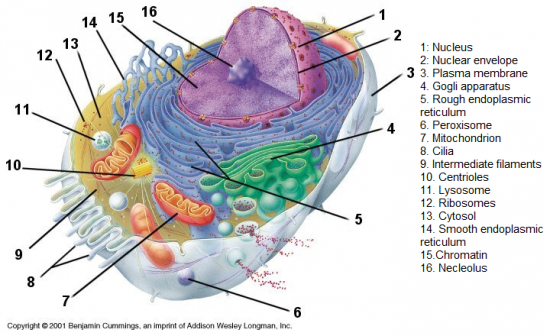 |
|
What are the three major structures of a cell?
|
Nucleus, Cytoplasm (H2O, and organelles), Plasma membrane
|
|
What does the nucleus do?
|
Controls cell division
Controls protein synthesis Contains DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) |
|
What are organelles?
|
"little organs" within the cytoplasm that perform specific task associated with cell function
|
|
What are the different organelles?
|
Cytoskeleton
Mitochondria Ribsosomes Endoplasmic reticulum Gogli apparatus Lysosomes |
|
Describe the cytoskeleton.
|
Gives cells shape and movement
e.g. in muscles : made up of protiens call actin and myosin FIG 3.7 pg 72 |
|
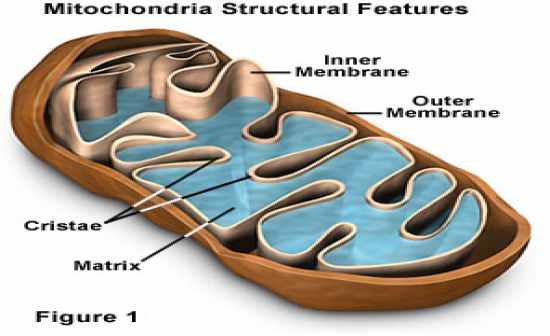
Descirbe mitochondria.
|
Generation of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) energy using glucose and oxygen and releases carbon dioxide and water
|
|
What does the root word cyto mean?
|
Cell
|
|
What does the root word plasm mean?
|
Fluid
|
|
Draw a mitochondrion
|
 |
|
What is the function of a ribosome.
|
It is the site of protein synthesis.
Makes proteins by joining amino acids together. |
|
What is ER and its function?
|
Rough Endoplasmic retiulum: Has ribosome attached and modify protiens.
Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum: is where lipid metabolism occures, detoxification and storage of certain ions and minerals such as Ca2+ |
|
What is the function of the Gogli Complex?
|
Modifies concentrates and packages proteins and lipids
Adds or removed sugars Is the highway for proteins - Complete product moved in secretory vesiles to eith become part of the cell/ be secreted from the cell or remain in the cell |



