Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
9.1.1:
State the independence of the vertical
and the horizontal components of
velocity for a projectile in a uniform
field.
|
Simple state objective.
|
|
9.1.2: Describe and sketch the trajectory of
projectile motion as parabolic in the
absence of air resistance.
|
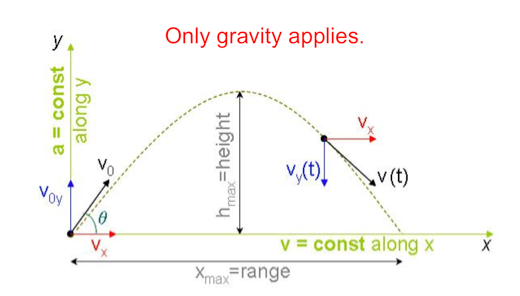 Refer to image. |
|
9.1.3:
Describe qualitatively the effect of
air resistance on the trajectory of a
projectile.
|
Effects include a shorter range and a lower maximum height attained during flight. Caused by drag force opposing projectile motion. Air resistance is this cause.
|
|
9.2.1: Define gravitational potential and gravitational potential energy.
|
1.
Gravitational Potential Energy (EP) - the work done bringing a small point mass in from
infinity to a point in a gravitational field (NOTE:
the work done is path independent)
2.
*Gravitational Potential (V) – the work done per unit mass bringing a small point
mass in from infinity to a point in a gravitational field (NOTE: the work done is path independent)
|
|
9.2.2: State and apply the expression for gravitational potential due to a point mass.
|
Gravitational Potential:
V = W / m
= -GMe / r
Gravitational Potential Energy:
PE = △Ep
= mg△h
= m△V
= -GMem / r
|
|
9.2.3: State and apply the formula relating gravitational field strength to gravitational potential gradient.
|
Gravitational Field Strength (I)
= - ΔV / Δx
|
|
9.2.5: Describe and sketch the pattern of equipotential surfaces due to one and two point masses.
|
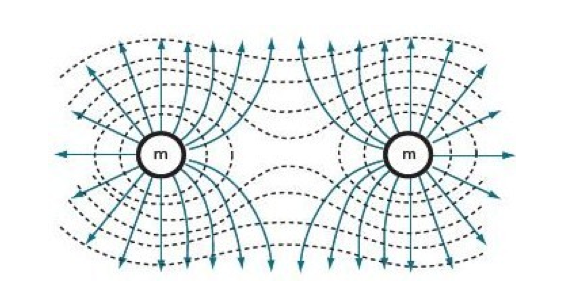 1. Equipotential Surface – a surface on which the potential is the same everywhere |
|
9.2.6 State the relation between equipotential surfaces and gravitational
field lines.
|
Gravitational lines ⊥ equipotential surface
|
|
9.2.7 Explain the concept of escape speed from a planet.
|
² The minimum initial speed at surface of a body required to escape a body’s gravitational field.
² M IS BEG:
Minimum Initial
Speed for Body to Escape Gravitational
field
|
|
9.2.8 Derive an expression for the escape speed of an object from the
surface of a planet.
|
|KE| = |PE|
|0.5mvescape2|
= |-GMem/Re|
vescape = √2GM/R
vescape on earth = √2g0Re
( g0 = GMe / Re2) |
|
9.3.1 Define electric potential and electric potential energy.
|
1.
Electric Potential (V) -
work done per unit charge moving a small positive test charge in from
infinity to a point in an electric field. (V = W/q) (V = kq/r) (NOTE: the work done is path
independent)
2.
*Electric Potential Energy (Ee)- energy that a charge has due to its position in an
electric field
|
|
9.3.2 State and apply the expression for electric potential due to a point
charge.
|
The
path taken does not affect the work done.
Work
done will equal the change in potential energy.
Work done = Final Ep – Initial Ep = Vyq - Vxq |
|
9.3.3 State and apply the formula relating electric field strength to electric
potential gradient.
|
Potential gradient:
Work
done to move a charge from one potential to another
= qΔV W = FΔx FΔx = qΔV |
|
9.3.4 Determine the potential due to one or more point charges.
|
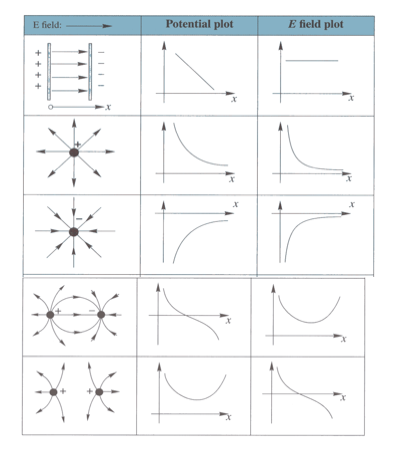 See image. |
|
9.3.5 Describe and sketch the pattern of equipotential surfaces due to one
and two point charges.
|
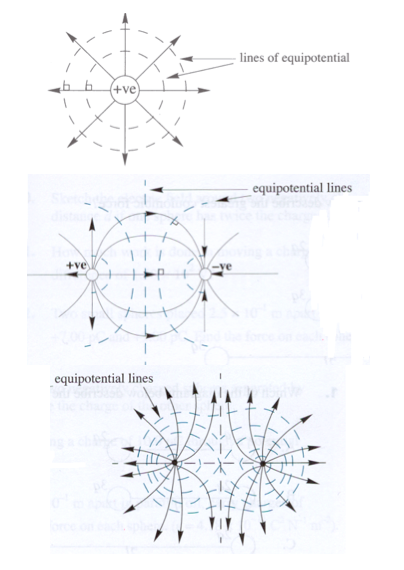 See image. |



