Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Engineering stress
|
Sigma=F/Ao
|
|
Engineering strain
|
E=(L-Lo)/Lo
|
|
Modulus of Elasticity
|
E=sigma/e
|
|
Yeild point
|
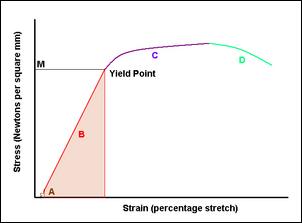 A strength characteristic of the material, aka yeild strength |
|
Tensile strength
|
Top of plastic portion of curveTS=Fmax/Ao
|
|
Necking
|
The portion of the elastic curve to the right of TS.
|
|
Ductility
|
The amount of strain that a material can endure before failure. The ability to plastically strain without fracture. Can be calculated with elongation or area reduction.
|
|
True stress-strain
|
If actual (instantaneous) area (for stress) or length(for strain) that becomes increasingly smaller as the test proceeds
|
|
Toughness
|
The ability of material to absorb energy. Roughtly the area under the stress/strain curve
|
|
Work hardening
|
AKA strain hardening, the metal becomes stronger as the strain increases
|
|
What happens when true stress strain of the plastic region of the curve is plotted against log-log time
|
It has a linear relationship
|
|
Hardness
|
Resistance to permanent indentation. Resistant to scratching. Strong correlation between hardness and strength.
|
|
If you just consider density and strength, what material is preferrable over what?
|
Aluminum is prefferable, however, iron and steel are less expensive.
|
|
List five metals in order of strength
|
Aluminum, aluminum alloys, cast iron, steel, titanium alloys
|
|
As steel strength increases
|
Castability, weldability, formatbility, machinability, manufacturability all decrease.
|



