Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What is the medical definition of diarrhea?
|
Increase in daily stool weight above 200 grams
|
|
9 L of fluid enters the intestines daily, where does it come from?
Where does it go? |
2 L oral intake
1 L saliva 2 L gastric secretions 4 L pancreatic, biliary, intestinal secretions 7 L absorbed by SI 1-2 L absorbed by colon (stool output 100-200 g daily) |
|
Most cases of acute diarrhea are likely caused by what etiology?
|
Viral, because stool cultures positive only in 1-6% of cases
|
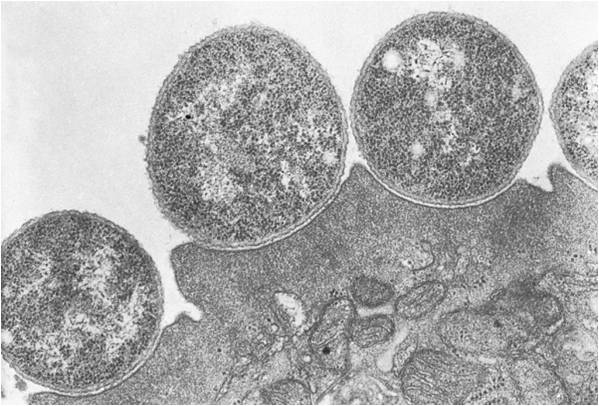 What organism is this, and what mechanism causes diarrhea in the host? |
E. coli (EPEC)
Adherence |
|
Name 4 infectious agents that cause diarrhea by adherence
|
EAggEC
EPEC Giardia Cryptosporidium (Adherence = Cr. E. EP. Guy) |
|
Name 3 bacteria that release preformed toxin
|
Bacillus cereus
Clostridium perfringens Staph aureus (Preformed = BCS) |
|
Name 2 bacteria that release enterotoxin
|
Vibrio cholera
ETEC (puppy gets Enterotoxin = enter the V ET ' s office) |
|
Name 3 pathogens that cause minimal mucosal invasion
|
Rotatvirus
Adenovirus Norwalk virus (Minimal = these caused damage, then RAN away) |
|
Name 3 that cause Variable mucosal invasion
|
Camplyobacter
Salmonella Vibrio parahemolyticus (Variable = feel it in your Vi S C era) |
|
Name 3 that cause Severe mucosal invasion
|
Shigella
Entamoeba histolytica EIEC (Severe = you can SEE blood) |
|
Name two organisms that can cause Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome or Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura, particularly in the young and elderly
|
E. Coli O157:H7 (EHEC)
Shigella |
|
What is the classic triad of Reiter's syndrome?
What infectious agent of diarrhea is associated with Reiter's? |
Conjunctivitis, Urethritis, Arthritis (Can't see, Can't pee, Can't climb a tree)
Yersinia |
|
Food poisioning symptoms within ___ hours of exposure suggest ingestion of preformed toxin
Symptoms within ___ hours suggest C. perfringens Symptoms ___ hours could be viral or bacterial |
6
8-16 >16 |
|
What is the classic epidemiological clue for each pathogen?
1. S. Aureus 2. B. Cereus 3. E. Coli O157:H7 4. Rotavirus 5. Norwalk virus (Norovirus) 6. Salmonella 7. V. parahemolyticus 8. C. dificile |
1. Potato salad
2. Fried rice 3. Undercooked meat 4. Daycare 5. Cruise ship 6. Poultry, lettuce 7. Shellfish 8. Antibiotics/hospitalization |
|
Which is a better test: Fecal leukocytes or Fecal lactoferrin?
|
Fecal lactoferrin (S/SP 90-100) but it is not widely available
|



