Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
 Internal buds found in freshwater sponges that are the result of asexual reproduction |
gemmules
|
 The free-swimming flagellated larva of many sponges produced as the result of sexual reproduction. |
amphiblastula
|
 Structural support for Porifera, may be made of silica or CaCO3. |
Spicules
|
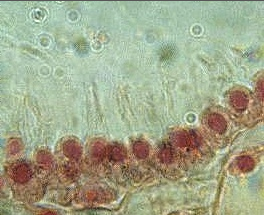 What is this structure found in sponges and what is its function? |
choanocytes used in capture and filtering of small food particles.
|
|
Body plan of a sponge characterized by a stalk-like spongocoel surrounded by a single layer of choanocytes.
|
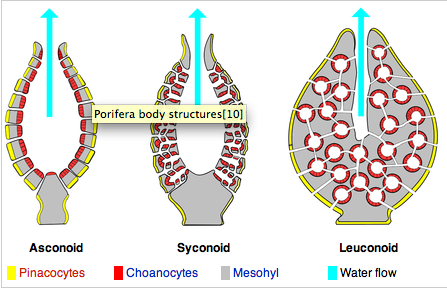 Asconoid |
|
The most complex body form of a sponge. The canal system is extensively branched. Small incurrent canals lead to flagellated chambers lined by choanocytes.
|
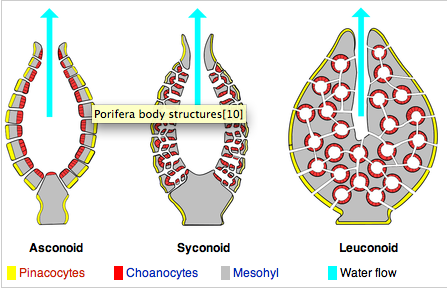 Leuconoid |
|
Tubular body plan similar to the ascon sponge, but the body wall is folded. The "folds" form radial canals.
|
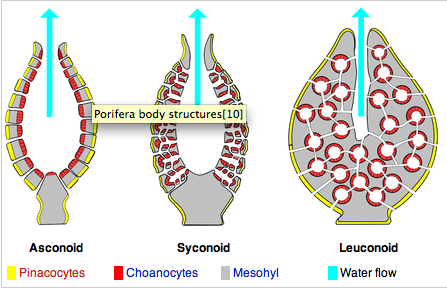 Syconoid (ex. Grantia) |
|
Material of fiber network in Euspongia that makes it usable as bath sponges
|
Spongin
|
|
Path of water currents in Synconoid sponges
|
Prosoplye ->flagellated chamber -> apopyle -> osculum
|
|
What are parazoa?
|
 Organism classified in the subkingdom parazoa exhibit differentiated cells but not true tissues. |
|
What are the two means of asexual reproduction in sponges?
|
Gemmules and budding
|
|
Examples of hydrozoans.
|
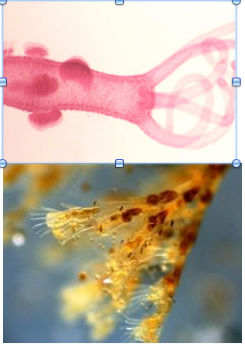 Hyrda (freshwater), Obelia (colonial) |
|
Characteristics of scyphozoans
|
Marine, nematocysts capture prey,
|
|
2 phases of cnidarian life cycle
|
Asexual polyp and sexual medusa (no medusa in anthozoans)
|
|
Definition of zooid
|
One of the distinct individuals forming a colonial animal such as a bryozoan or hydrozoan
|



