Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
List the key hormones and their function for regulating the CV system.
|
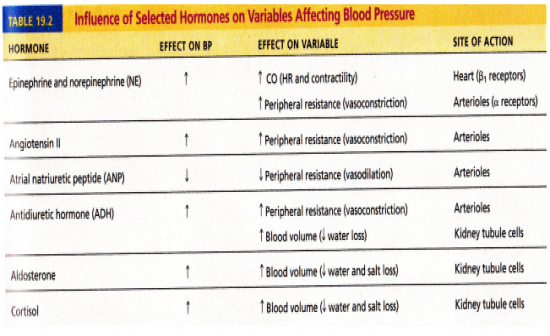 - Epinephrine & norepinephrine: Increase BP - Angiotensin II: Increase BP - Antidiuretic Hormone (Vasopressin): Increase BP - Aldosterone: Increase BP - Cortisol: Increase BP - Atrial natriuetic peptide (ANP): Decrease BP See table for more detail |
|
Draw the bodies compensatory response to a decrease in blood pressure and blood volume.
|
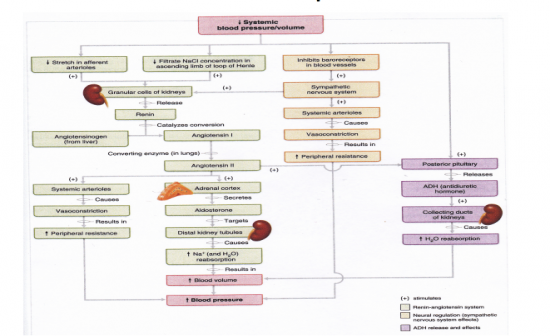 See Image |
|
Name 3 stimuli to increase renin secretion:
|
Any three of the following: Anything that results in a fall in blood pressure will stimulate renin secretion:
- Sodium depletion - Dehydration - Haemorrhage - Hypotension - Diuretics - Upright position |
|
What is the actionof Angiotensin II on vascular smooth muscle cell?
|
Contraction
|
|
What is the action of Angiotensin II on peripheral sympathetic nerve terminals?
|
Increases effector cells of nor adrenaline. Hence angiotensin II acts to strengthen the response of Nor adrenaline also negative feedback with noradrenaline.
|
|
What two receptors control the secretion of Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)?
|
Both found in hypothalamus:
1. Osmoreceptors 2. Baroreceptors |
|
Describe the effect of increased osmotic pressure of extracellular fluid:
|
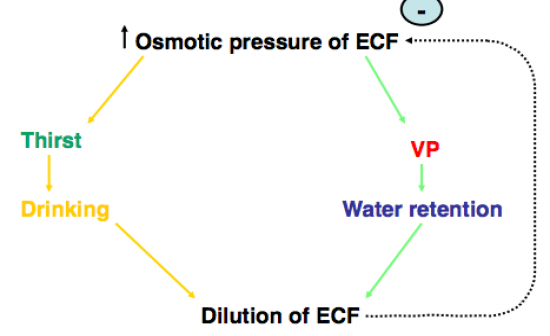 See image: |
|
Describe the pathway for the action of Aldosterone.
|
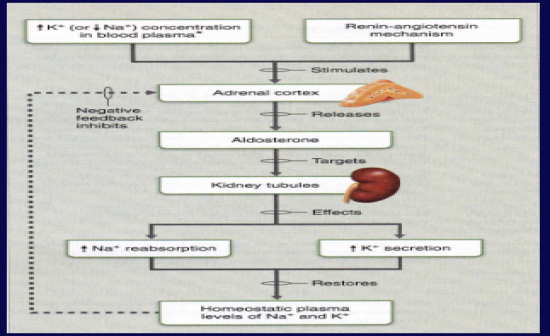 Aldosterone acts on the tubules of the kidneys to increase Na+ reabsorption (and hence water reabsorption) and K+ secretion, resulting in a return of normal homeostatic levels of Na and K, and returning blood volume to normal. See Image: |
|
What is the key negative rehulator of this system? (decrease blood volume and pressure)
|
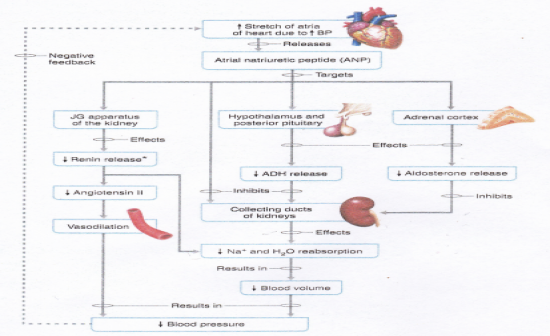 Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP): - Negative inhibition of renin, ADH, aldosterone - Vasodilation - Decreased Na+ and water absorption Hence reduces blood volume and pressure See Image: |
|
How does ANP work?
|
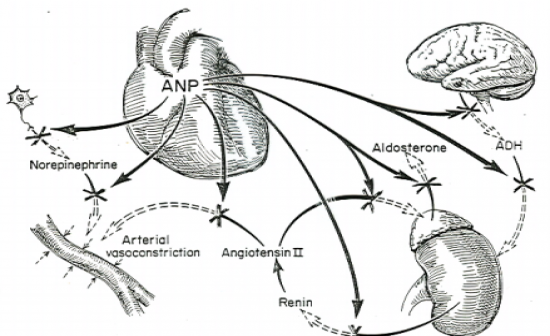 ANP inhibits all events that promote vasoconstriction & Na+ and water retention. Hence having opposite effect to result in a decrease in blood volume and blood pressure. See Image: |
|
Main action of Kinin-Kallikrein?
|
Main role is to relax the vascular smooth muscle cells and hence decrease blood pressure.
|
|
What are the local effects of kinin antagonist?
|
To increase blood pressure.
|
|
List two main catecholamines and their action on the arterioles:
|
1) Adrenaline (epinephrine): Vasoconstriction (skin, kidney) and Vasodilation (skeletal muscle, liver, coronary) - redistributes blood flow
2) Noradrenaline (norepinephrine): Vasoconstriction |
|
List two main catecholamines and their action on the heart:
|
Both adrenaline and noradrenaline: Increase force of contraction
Adrenaline: Increases heart rate and cardiac output. |
|
List two main catecholamines and their action on blood pressure:
|
Both adrenaline and noradrenaline increase systolic pressure.
Noradrenaline increases diastolic pressure Adrenaline decreases diastolic pressure |



