Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What is MHN?
|
“Mental health is a branch of nursing concerned with the prevention and treatment of mental disorders and their symptoms”
|
|
professional bodies and practice standards for MHN
|
- AHPRA (Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Authority)
- NMBA (Nursing and Midwifery Board of Australia) |
|
Describe the continuum of mental illness-mental health
|
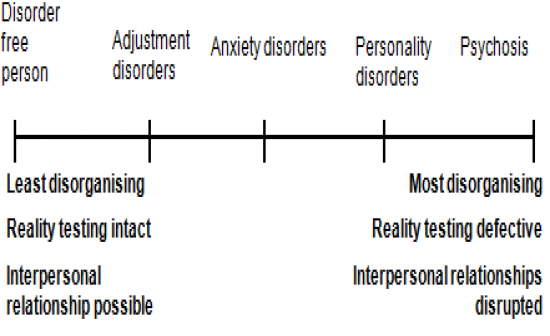 |
|
State the Characteristics of a mentally healthy individual
|
ü Realizes own abilities
ü Can cope with normal stressors of life ü Can work productively/ fruitfully ü Able to contribute to their community |
|
Differentiate between a mental health problem and a mental disorder
|
Mental Health PROBLEM:is a problem that does not meet the criteria for a Mental Disorder (e.g. worry and sadness)
Mental DISORDER:is adiagnosable illness that significantly interferes with an individual’s cognitive, emotional or social abilities |
|
Differentiate between nursing diagnoses and DSM-IV-TR diagnoses
|
NURSING DIAGNOSES:most mental health nurses translate behaviors into a nursing diagnosis by relating the behavior to the cause e.g. refusing food (behavior) related to fear that food is poisoned (cause).
DSM-IV-TR DIAGNOSES:The DSM IV TR system is descriptive, it is based on symptoms rather than the cause, it gives a systematic description associated features, specific age, cultural & gender related features, prevalence, incidence, risk, predisposing factors, familial pattern, course, complications, and differential diagnosis, with a diagnostic criteria specific to each disorder. |
|
Axis I
|
Clinical disorders and other disorders that may be a focus of clinical attention
- includes all psychiatric disorders except personality disorders and mental retardation - 17 categories: mood disorders, anxiety disorders etc |
|
Axis II
|
Personality disorders and intellectual disability (mental retardation
|
|
Axis III
|
Physical disorder or general medical condition that is present in addition to the mental disorder
- may be causative, consequential or unrelated to the mental disorder |
|
Axis IV
|
Psychosocial and environmental problems that contribute to the development or exacerbation of the disorder, may be positive or negative stressors
|
|
Axis V
|
Global assessment of functioning (GAF) scale
|
|
Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF)
|
Is a reflection of the evaluating clinician's judgment of a patient's ability to function in daily life. The 100 point scale measures psychological, social and occupational functioning
|
|
List predisposing and precipitating factors implicated in the causation of mental disorder i.e. Nature v Nurture
|
A predisposing factor is something present before the development of a disorder that places a person at higher risk of developing it. A precipitating factor is a stressor implicated in the development of a disorder such as bereavement.
1. Organic factors (nature)involve biological and genetic factors such as degeneration, trauma, poisons, infections and vitamin deficiencies. 2. Functional factors (nature/psychological)involve personality type, psychological defences, locus of control and self perception. Socio-cultural factorsinvolve cultural background, social position, bereavement, disasters, developmental transitions and gender |
|
List factors that prevent and/or reduce the incidence, or limit the severity of mental disorders
|
V Individual factors:temperament, coping style, attachment to family, intelligence, optimism.
v Family factors:supportive, caring parents; secure, safe family; stable family; supportive relationship with another adult. v School Context: sense of belonging, positive school climate, school against violence. v Life events and situations:economic security, good physical health, opportunities at critical life transitions. v Community and Cultural:sense of connectedness, attachment and networks within the community, strong cultural identity, access to support services. |
|
Acculturation
|
The process of assimilating new ideas into an existing cognitive structure
|



