Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What enters the patient?
|
X-ray beam
|
|
The x-ray beam that exits the patient is captured by what?
|
Some form of an image receptor
|
|
What is needed to produce x-rays?
|
A source of Electrons(comes from the filament/ Cathode)
|
|
What is needed to cause the e-stream to accelerate at an extremely high speed from the cathode to the anode?
|
High Voltage (KVp)
|
|
What do the stream of electrons need to do in order to produce an x-ray?
|
Slow down
|
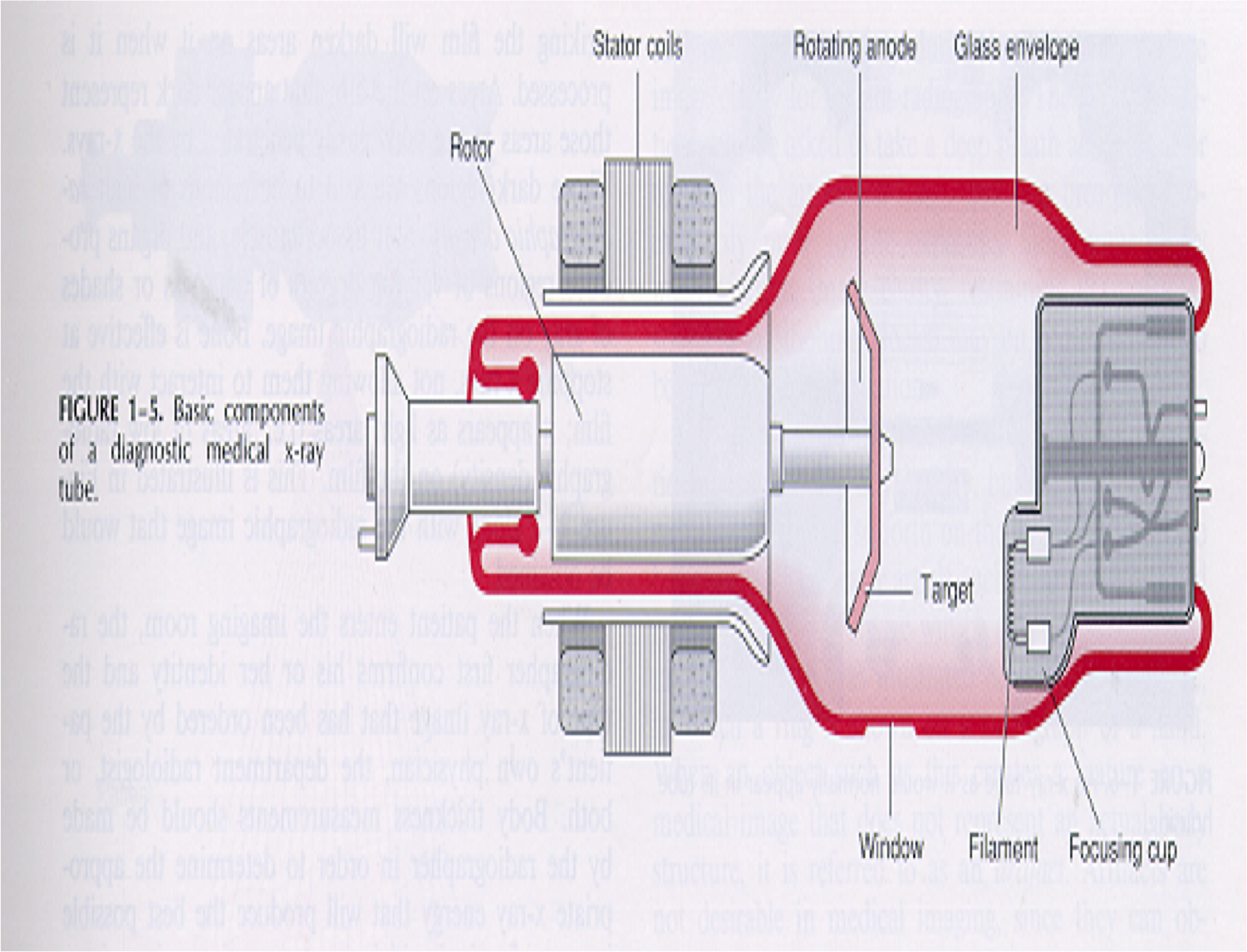 Explain the pic of the x-ray tube |
RotorStator CoilsRotating Anote (positive)Glass EnvelopeCathode Focusing Cup (negative) Filament (negative)WindowTarget
|
|
What are (6) characteristics of x-rays?
|
Photons/ bundles of energyhighly penetratingInvisibletravel at the speed of light (186,000 miles/sec)travel in straight lines, but diverge from point of originHave different energies
|
|
What are major types of image receptors?
|
Film/screenDigitalFluoroscopic
|
|
What is the primary beam?
|
The x-ray beam that exits the x-ray tube
|
|
How many photons does the primary beam consist of?
|
A multitude; millions
|
|
Where does the primary beam exist?
|
Between the Tube and the Patient
|
|
What is the primary beam made up of?
|
Photons of many different energies
|
|
What is the remnant beam?
|
What remains after it passes through the patient
|
|
What does the remnant beam do?
|
Produces the image
|
|
What is scatter Radiation?
|
X-ray photons that, while passing through the patient, interact in such a way to cause them to be diverted from their normal path
|



