Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
1. The amplitude of a sound is the
a. amount of sound energy falling on a unit area. b. intensity of the sound. c. magnitude of displacement of a sound pressure wave. d. psychological aspect of sound related to frequency. e. pitch. |
C
|
|
2. Frequency is usually measured in units called
a. mm. b. Hz. c. mL. d. dB. e. arcmin. |
B
|
|
3. _______ is the psychological aspect of sound related to perceived intensity or
magnitude. a. Loudness b. Pitch c. Frequency d. Intensity e. Tone |
A
|
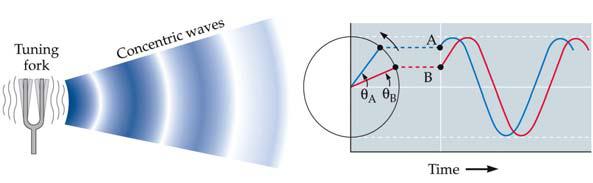 4. The figure below depicts the simplest kind of sound, known as a a. simple sound. b. sine wave. c. period. d. phase. e. tone. |
B
|
|
5. A complex tone is a sound wave consisting of
a. more than one sinusoidal component of different frequencies. b. several cycles. c. phases. d. periods originating from the same sinusoidal component. e. cycles at more than 1000 Hz. |
A
|
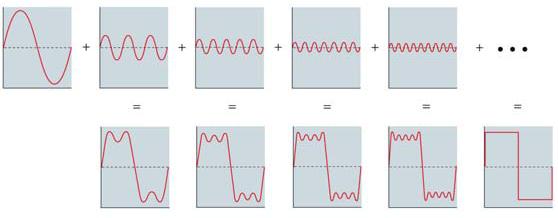 6. The figure below shows the composition of a. sine waves. b. simple sounds. c. complex sounds. d. sinusoidal components. e. reticulated waves. |
C
|
|
7. The purpose of the ear canal is to
a. transmit information from the brain back to the ear. b. transduce sound waves into electric signals. c. prevent damage to the tympanic membrane. d. keep the pressure inside the ear comfortable. e. All of the above |
C
|
|
8. The _______ consists of three tiny bones called ossicles.
a. tympanic membrane b. middle ear c. inner ear d. cochlea e. outer ear |
B
|
|
9. One of the roles of the ossicles is to
a. amplify sounds. b. protect the ear canal. c. vibrate continuously. d. transmit sound waves back to the environment. e. All of the above |
A
|
|
10. The acoustic reflex protects the ear from intense sounds by
a. transmitting only low-frequency sounds to the brain. b. contraction of the stapedius and tensor tympani muscles. c. opening the oval window to transmit vibration. d. transmitting loud noises back to the ear canal. e. stiffening the round tympanic membrane. |
B
|
|
11. The _______ is the location where fine changes in sound pressure in the environment
are translated into neural signals. a. outer ear b. middle ear c. inner ear d. tympanic canal e. oval window |
C
|
|
12. Vibrations transmitted through the tympanic membrane and middle-ear bones cause
the _______ to push and pull the flexible window in and out of the vestibular canal at the base of the cochlea. a. helicotrema b. basilar membrane c. round window d. stapes e. pinna |
D
|
|
13. The organ of Corti is a structure on the basilar membrane composed of _______ and
dendrites of auditory nerve fibers. a. hair cells b. tiny bones c. fluid-filled chambers d. muscles e. mucous |
A
|
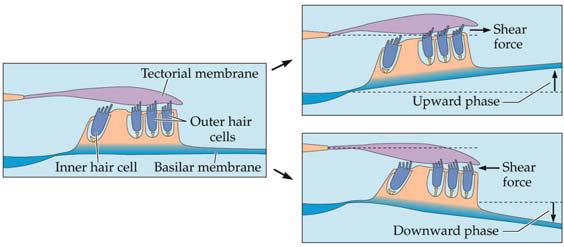 14. The figure below shows what happens when _______ causes a displacement along the cochlear partition. a. neural firing b. the auditory system c. vibration d. place code e. head tilt |
C
|
|
15. Most of the information about sound waves is conveyed to the brain by the
a. outer hair cells. b. inner hair cells. c. cochlear membrane. d. tympanic membrane. e. oval window. |
B
|



