Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
General senses
|
Large group of touch receptors
|
|
Special senses
|
Taste, smell, sight, hearing, and balance
|
|
Localized receptors
|
Confined to head region; receptors aren't free endings of sensory neurons
|
|
-Specialized receptor cells
|
Neuron-like epithelial cells or small peripehral neurons
|
|
Taste
|
-gustation
-receptors classifed as "chemoreceptros" that respond to food dissolced in saliva fluids |
|
Superior surface of tongue
|
-stratified squamons epithelium
-filiform papillae -fungiform papillae -vallate papillae -sulcus terminalis: marks border between mouth and pharynx -Lingual tonsil: covers posterior 1/3rd of tonge that lies in oropharynx |
|
Superior surface of tongue image
|
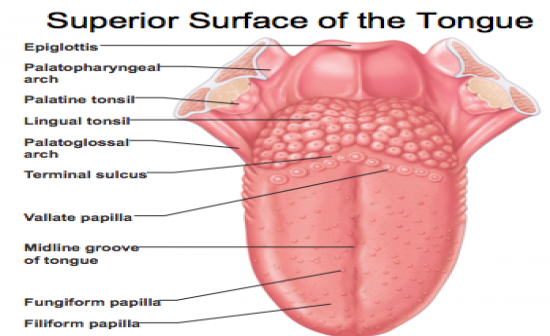 |
|
Filiform papillae
|
-most numerous papillae on tongue are small and concial pointed in shape and line up in parallel rows which enable tonge to grasp and manipuate food; DON'T contain tate buds
|
|
Fungiform papillae
|
Mushroom shapd and spread over anterior 2/3rd of tongue on surface; contain taste buds
|
|
Vallate papillae
|
V-shaped row bordering the posterior third of the tongue and directly anterior to the terminal sulcus (sulcus terminalis) groove; contain taste buds
|
|
Taste buds
|
-contain taste receptors
-collection of 50-100 epithelial cells -contain two major cell types -> Gustatory epithelial cells -> Basal epithelial cells -contain long microvilli (gustatory hairs): extend trhough a taste pore to the surface of the epithelim -Cells in tastebuds replaced every 7-10 days |
|
Taste Sensation and Gustatory Pathway
|
-Five basic qualities of taste: sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami; "umami" elicited by glutamate
-Taste map is a myth -all taste modalities can be elicited from all areas of tongue containg taste buds (fungiform and vallate papillae) |
|
Gustatory Pathway
|
-Taste information reaches the cerebral cortex primarily through the facial (CN VII), glossopharyngeal (CN IX) and vagus nerve (CN X)
-bitter taste receptors ahve been found in stomach -Gustatory sensory neurons synapse in which solitary nuclues of medulla from which impulses are transmitted to teh thalamus and ultimately to the gustatory area of the cerebral cortex in insula |
|
Smell
|
-olfaction
-Receptors: classified as "chemoreceptors" that resond to airborne chemical that dissolve in fluids of nasal mucosa |
|
Olfaction
|
-olfactory receptors are part of the olfactory epithelium
-Olfactory epithelium is pseudostratified simple columan and contains three main cell types ->olfactory sensory neurons ->supporting epithelial cells ->basal epithelia cells |



