Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What is the core structure of tetracyclines?
|
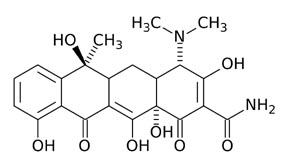 Four fused 6-membered rings (tetra-cycline). |
|
What is the main structural modification to the tertracycline structure that yields tigecycline?
|
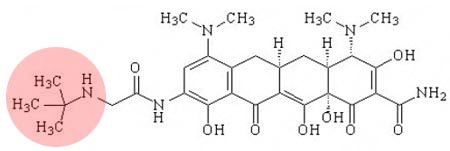 Glycoamino complex. |
|
How do tetracyclines (and tigecyline) work?
|
They inhibit protein synthesis by binding to the 30S bacterial ribosomal subunit.Note: Tigecyline binds more strongly
|
|
Tetracyclines used to be considered broad-spectrum antibiotics. What changed?
|
Widespread resistance limits their use.
|
|
Are tetracyclines (and tigecyline) bactericidal or bacteriostatic?
|
Bacteriostatic.
|
|
What are mechanisms of resistance to tetracyclines? What about tigecycline?
|
1. EFFLUX (main mechanism): both Gram+ and Gram- can synthesize large amounts of efflux proteins2. Ribosomal Protection Proteins: bacteria can produce proteins that bind to the ribosome, causing a conformational change so that tetracylines can not longer bind.3. Decreased penetration across bacterial membrane
Tigecycline is less susceptible to resistance; tet-resistant organisms are susceptible to tigecycline. |
|
How are tetracyclines administered and absorbed? What about tigecycline?
|
Tetracyclines are administered orally, with variable absorption. Absorption is impaired by di-and trivalent cations, e.g. Ca2+ (don't take with milk), Mg2+, Al3+ (component of antacids).
Tigecycline is administered by IV. |
|
How is tetracycline distributed in the body?
|
Sequestered in tissues, usually liver. This means Vd can be bigger than body water. Concentration in CSF is low.
|
|
How are tetracyclines metabolized and eliminated?
|
Tetracyclines are concentrated in the liver.
Primary elimination route varies: - Doxycycline and minocycline ("domino") eliminated hepatically. Use these for renal failure patients.- Demeclocyline and tetracycline eliminated renally Note: t1/2 of doxycyline (16hrs) is twice as long at t1/2 of tetracyline (8hrs), which makes doxycyline very popular. |
|
What are tetracyclines used for?
|
Since broad spectrum activity has been largely compromised by resistance, tetracyclines are good for organisms that lack a cell wall.-- Rickettsiae-- Chlamydiae-- Lyme disease
|
|
What are some adverse effects of all tetracyclines?Specific tetracyclines?
|
1. GI irritation2. Effects on calcifying tissues (they bind Ca2+)-- inhibit bone growth in utero (contraindiated in pregnant women, children <8yo)-- discoloration of teeth3. Hepatotoxicity (especially in pregnant women)4. Decreased efficacy of oral contraceptives5. Can lead to superinfections by broadly killing off flora
*6. Democlo- and doxycline can lead to photosensitiviy ("phoDosensiDivity")*7. Minocyclin can lead to dizziness |
|
What are two reasons tetracycline is contraindicated in pregnant women?
|
1. Inhibition of fetal bone growth2. Increased susceptibility to hepatotoxicity in both mother and fetus.
|
|
Who may not take tetracyclines due to its effect on calcifying tissues?
|
Pregnant women and children under 8yo.
|
|
What are some adverse effects of tigecycline?
|
FeverGI irritationHypertensionHepatotoxicityHematologic
Alphabetical: FGHHH |
|
What are differences between tetracyclines and tigecyline?
|
Administration: tetracyclines are given orally, tigecycline by IV
Efficacy: tigecyline binds better to 30S subunit AND evades resistance mechanisms Clinical uses: Tetracyclines have some broad spectrum activity (diminished due to resistance) and are effective against organisms that lack a cell wall. Tigecycline is reserved for complex skin and intra-abdominal infections and drug-resistant organisms. Adverse Effects: lots for tetracyclines, few for tigecyline |



