Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Amino acids and 3 letter codon
|
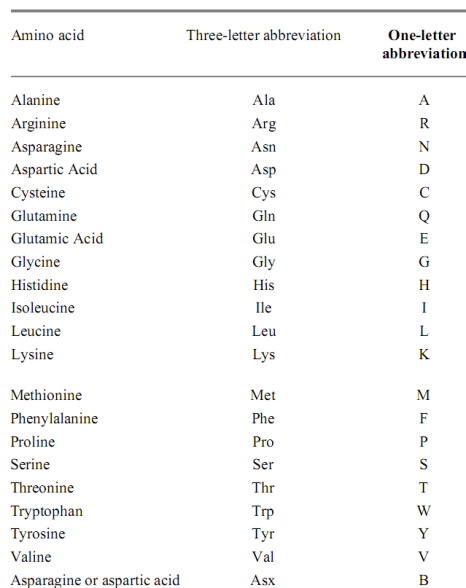 |
|
Amino
Acid Structure and Function
|
Although
more than 300 different amino acids have been described in
nature, only twenty are commonly found as constituents of mammalian proteins. Each amino acid(except for proline) has a carboxyl group, an amino group, and a distinctive side chain ("R-group") bonded to the a-carbon atom . At physiologic pH (approximately pH = 7.4), the carboxyl group is dissociated, forming the negatively charged carboxylate ion (-COO ), and the amino group is protonated (-NH3+). |
|
Amino acids with nonpolar side chains:
|
Each of these amino acids has a nonpolar side chain that does not bind or give
off protons or participate in hydrogen or ionic bonds. The side chains of these
amino acids can be thought of as "oily" or lipid-like, a property
that promotes hydrophobic interaction.
|
|
Amino acids with uncharged polar side chains :
|
These amino acids have zero net charge at neutral pH, although the side chains
of cysteine and tyrosine can lose a proton at an alkaline pH. Serine,
threonine, and tyrosine each contain a polar hydroxyl group that can
participate in hydrogen bond formation. The side chains of asparagine and
glutamine each contain a carbonyl group and an amide group, both of which can
also participate in hydrogen bonds.
|
|
Amino acids with acidic side chains:
|
The amino acids aspartic and glutamic acid are proton donors. At neutral pH,
the side chains of these amino acids are fully ionized, containing a negatively
charged carboxylate group (-COO"). They are,therefore, called aspartate or
glutamate to emphasize that these amino acids are negatively charged at
physiologic pH.
|
|
Amino acids with basic side chains:
|
The side chains of the basic amino acids accept protons. At physiologic pH the
side chains of lysine and arginine are fully ionized and positively charged. In
contrast, histidine is weakly basic, and the free amino acid is largely
uncharged at physiologic pH. However, when histidine is incorporated into a
protein, its side chain can be either positively charged or neutral, depending
on the ionic environment provided by the polypeptide chains of the protein.
All free amino acids, plus charged amino acids in peptide chains, can serve as buffers. |
|
General facts of amino acids
|
Amino acids are the building blocks of protein. When you eat a
food that is high in protein, your body digests the protein into individual
amino acids and short links of amino acids that are small enough to be absorbed
into the bloodstream. The primary functions of amino acids are to build and
repair muscle tissue, but the benefits go beyond that. These things produce
chemicals that allow our brains to function at its highest potential
|



