Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
The Plasma Membrane
|
 The boundary that separate the living cell from its nonliving surroundings; regulates the traffic of chemicals in and out of the cell; made up of lipids and proteins; has a phospholipid bilayer- hydrophoic tails, hydrophilic heads; inside membrane- proteins help to regulate traffic across membrane; a fluid mosaic |
|
Nucleus
|
 The genetic control of the cell; bordered by a double membrane called the nucleolus (pores allow certain materials to pass between the nucleus and the cytoplasm); inside: long DNA molecules and protein from fibers called chromatin (chromosomes); nucleolus- where the components of the ribosomes are made. |
|
Ribosomes
|
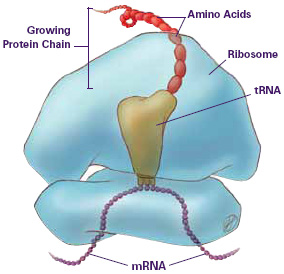 In the cell and outside of the nucleus; responsible for protein synthesis. In Eukaryotic cells: components of ribosomes are made in the nucleus and then transported through the pores of the nucleus into the cytoplasm. (some ribosomes are suspended in cytoplasm- make protein that remain in fluid, other ribosomes attach to outside of endoplasmic reticulum- make protein that is incorporated into membranes or secreted by the cell. |
|
The Endomembrane System
|
Manufactures and distributes cellular products; the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell is filled with organelle membranes- some are connected to each other (by membranes or transfer of membrane segments between them): Nuclear Envelope, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi Apparatus, Lysosome, Vacuole
|
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum
|
 One of the main manufacturing facilities within a cell; produces a large variety of molecules; connected to the nuclear envelope; forms tubes and sacs running through the cytoplasm; made up of the rough ER and the smooth ER |
|
Rough ER
|
Considered "rough" because of ribosomes that stud outside of the ER membrane; The ribosome builds the amino acid chain, the chain is pushed into
the ER. When the protein is complete, the rough ER pinches off a transport
vesicle. That vesicle, a small membrane bubble, can move to the cell membrane or the Golgi apparatus.
|
|
Smooth ER
|
Lacks ribosomes; many enzymes built into the smooth ER membrane; function: synthesis of lipids, creation of steroids, packages proteins, detoxification function
|
|
Transport Vesicles
|
Membranous spheres that bud from the ER and transports products to the Golgi Apparatus
|
|
Golgi Apparatus
|
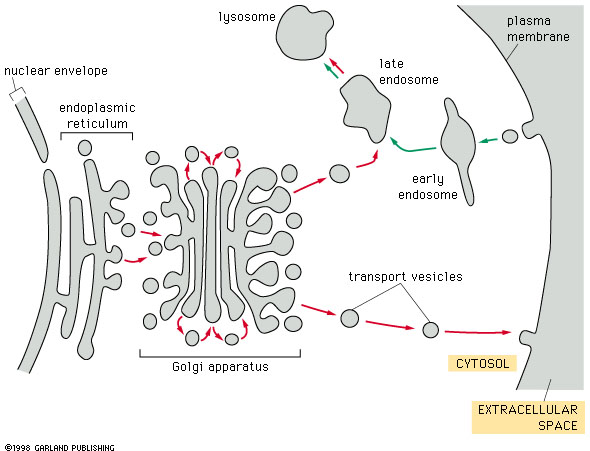 Refinery, warehouse, and shipping center; receives stores and distributes chemical products of the cell; products from the ER reach the Golgi in transport vesicles; One side of golgi stack serves as a receiving side; the shipping side is a depot from which finished products can be carried in transport vesicles to other organelles or to the plasma membrane; Enzymes within the Golgi modify the products of the ER during their move from the receiving to the shipping side. |
|
Lysosome
|
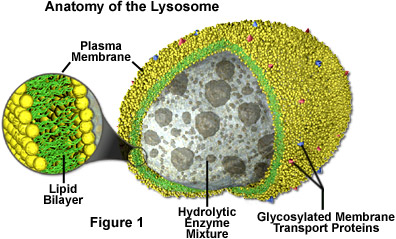 Ac of digestive enzymes found in animal cells; develop from vesicles that bud off from the Golgi; enzymes in a lysosome can break down large molecules such as polysaccharides, proteins, fats, and nucleic acids; provides a compartment for cell to digest molecules safely without unleashing digestive enzymes on the cell itself. Function: engulf nutrients into food vacuoles/ lysosomes fuse with vacuoles and expose food to enzymes to digest it/ amino acids result from this and leave to nourish the cell, break down large molecules of damaged organelles/makes molecules available for making new organelles, sculpturing function in embryonic development (webbed fingers)--> T-Sachs disease if missing digestive enzymes. |
|
Central vacuole
|
 Sacs that bud from the ER, Golgi or Plasma membrane; made up of water; gives cell its spherical structure |
|
Chloroplast
|
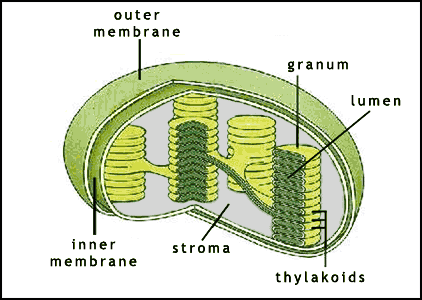 The food producers of the cell; does photosynthesis for cell; made up of stroma (area inside chloroplast where sugars are created-fluid) and one thylakoid stack is called a granum. The thylakoids have chlorophyll molecules on their surface. That chlorophyll uses sunlight to create sugars; absorb sunlight--> chemical E. |
|
Mitochondria
|
 The main function of the mitochondrion is the production of energy, in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The cell uses this energy to perform the specific work necessary for cell survival and function. Mitochondria are involved in building, breaking down, and recycling products needed for proper cell functioning. For example, some of the building blocks of DNA and RNA occur within the mitochondria. Mitochondria are also involved in making parts of blood and hormones such as estrogen and testosterone;converts chemical energy into usable energy; |
|
Cytoskeleton
|
 The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers throughout the cell's cytoplasm that helps the cell maintain its shape and gives support to the cell; A variety of cellular organelles are held in place by the cytoskeleton; make cells round; microtubules used for movement; microfilaments (smaller) |
|
Cilia and Flagella
|
 Extension of cell used for movement; cilia- protist lining respiratory tract and digestive tract |



